News Release
For immediate release: April 29, 2020
Contact: Michael Crusan
CWD investigation spurred by Douglas County deer farm detection concludes
The Minnesota Board of Animal Health’s investigation of all herds with connections to the CWD-positive Douglas County farm is complete and revealed a total of six CWD positive deer. In all, eight herds in six counties were linked by animal movement and six herds were quarantined. All the CWD positive deer were in two herds, the one in Douglas County and another in Pine County. With the investigation wrapped up, only one site has farmed cervids that remain quarantined in Chisago County.
“The quarantined herd will have a signed herd plan with the Board and will not move deer or related products onto or off of the farm during the agreement,” said Assistant Director, Dr. Linda Glaser. “The quarantine will be lifted in October 2022 if the CWD-exposed buck is alive and shows no clinical signs of CWD. The date is five years after the buck was exposed to known CWD positive does when it was in the Pine County herd.”
The investigated herds, test results and outcomes are broken down by the six counties in chronological order:
Douglas County: One doe died in late November and tested CWD positive. The remaining animal, a buck, was harvested and tested, with the result of CWD not detected. No deer remain on the farm and it’s quarantined for five years.
Pine County (two herds):
Herd 1: One doe died in December and tested positive for CWD. The producer accepted USDA indemnity for the herd, which was depopulated in January.
Eight deer were harvested and two does and two fawns tested CWD positive. No deer remain, the farm is quarantined for five years.
Herd 2: Herd closed before the investigation.
Clearwater County: One CWD-exposed animal was identified and it had been previously harvested and tested. CWD was not detected, and the quarantine was released.
Wadena County: Three CWD-exposed animals were identified and appraised by the USDA. Only two of the three deer could be found in the pen during the depopulation, and the third deer was never confirmed. The producer harvested the remaining two animals in the herd. CWD was not detected in any of the animals tested. No deer remain on the farm and because the CWD status of the third CWD-exposed animal could not be verified, the farm is quarantined for five years.
Chisago County (two herds):
Herd 1: Herd was identified with a CWD-exposed animal. The producer has not accepted USDA appraisal and indemnity, and the herd remains quarantined.
Herd 2: Herd closed before the investigation.
Kandiyohi County: Herd was determined to not be a source of CWD, and quarantine was released.
The Pine County, Douglas County and Wadena County sites are not allowed to have any deer or elk for five years. Owners must maintain fencing to prevent wild deer from accessing empty pens. Biohazard signs have been posted on the fencing and must be maintained for the entire five-year fallow period.
The Board’s investigation included reviewing and verifying herd histories, accuracy of records, identification tags, and meeting with the producers to inspect fencing and interview producers to gather information for USDA’s epidemiological questionnaire to identify risk factors for CWD exposure.
CWD is a disease of the deer and elk family caused by prions, which can damage brain and nerve tissue. The disease is most likely transmitted when infected deer and elk shed prions in saliva, feces, urine, and other fluids or tissues. CWD is not known to naturally occur in other animals. The disease is fatal in deer and elk, and there are no known treatments or vaccines. Consuming infected meat is not advised.
--30--
News Release
For immediate release: March 13, 2020
Contact: Erin Crider
Investigation confirms four additional CWD positive deer on Pine County farm
Test results from the depopulation of a Pine County deer farm have confirmed four additional cases chronic wasting disease (CWD). The first CWD positive animals at this farm were confirmed in January 2020, resulting in depopulation of the herd. This herd was investigated because it provided animals to a Douglas County deer farm in the past, including a CWD-positive doe that began the disease investigation in December 2019.
“This CWD investigation has gone very well,” said Board Assistant Director, Dr. Linda Glaser. “We identified the Pine County herd quickly from that initial positive result in Douglas County. We immediately traced animals and quarantined herds. Those actions were in coordination with other agencies to rapidly respond to CWD in Minnesota.”
In early December 2019, a doe from the Pine County herd died, was tested and found to be CWD positive. In January, two fawns were harvested, and one tested positive for CWD. Following this development, the remaining six deer in the herd were depopulated, all of which were submitted for CWD testing. Results from the National Veterinary Services Laboratory on these six deer confirmed the detection of CWD in two does and one fawn. In all, five of the nine total animals in the Pine County herd were CWD positive.
The Pine County and Douglas County sites are not allowed to have any deer or elk for five years. Owners must maintain fencing to prevent wild deer from accessing empty pens. Biohazard signs have been posted on the fencing and must be maintained for the entire five-year fallow period. The investigation is ongoing, and the Board will continue to take immediate action if any new detections are identified.
CWD is a disease of the deer and elk family caused by prions, which can damage brain and nerve tissue. The disease is most likely transmitted when infected deer and elk shed prions in saliva, feces, urine, and other fluids or tissues. CWD is not known to naturally occur in other animals. The disease is fatal in deer and elk, and there are no known treatments or vaccines. Consuming infected meat is not advised.
--30--
News Release
For immediate release: January 10, 2020
Contact: Michael Crusan
Investigation leads to additional CWD positive deer on Pine County farm
The ongoing chronic wasting disease investigation of farms tied to the Douglas County detection first reported in December 2019 has led to a CWD-confirmed doe on a Pine County farm. The herd in Pine County was being investigated because it provided animals to the Douglas County herd in the past, including the CWD positive doe that initiated the disease investigation.
“We identified the Pine County herd as high priority early in our investigation because our records showed it provided deer to the Douglas County herd,” said Board Assistant Director, Dr. Linda Glaser. “At this point in the investigation CWD has not been detected in any of the other herds connected to Douglas County.”
The Douglas County herd is completely depopulated, and the site is not allowed to have any deer or elk for five years. The owner must also maintain fencing to prevent wild deer from accessing the empty pen and post biohazard signs on the fencing for the entire five-year period.
The Pine County herd owner must also depopulate and test all remaining deer on the farm and maintain fencing with biohazard signage for five years. The investigation is continuing beyond this herd to discover additional movements of deer between it and other locations in the past. Any additional farms identified will be quarantined and their movement records will be reviewed.
CWD is a disease of the deer and elk family caused by prions, which can damage brain and nerve tissue. The disease is most likely transmitted when infected deer and elk shed prions in saliva, feces, urine, and other fluids or tissues. CWD is not known to naturally occur in other animals. The disease is fatal in deer and elk, and there are no known treatments or vaccines. Consuming infected meat is not advised.
--30--
News Release
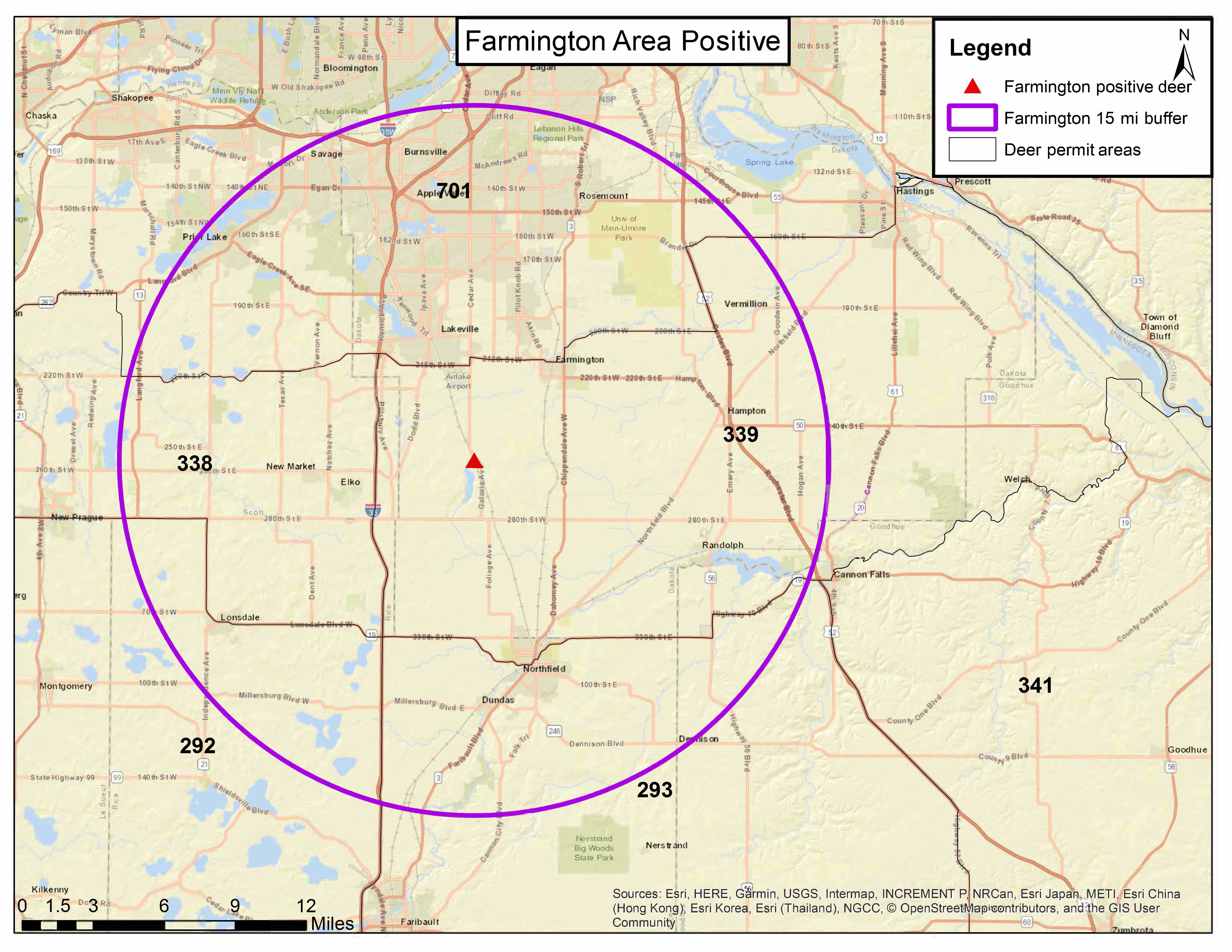
Wild deer in Dakota County confirmed positive for chronic wasting disease
March 13, 2020
Discovery marks first case of CWD in this area of Minnesota
A wild deer in Dakota County was confirmed positive for chronic wasting disease, the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources said.
The deer, an adult male, was reported by a local resident near Farmington as displaying neurological symptoms and was tested as part of the DNR’s risk-based disease surveillance program.
It is the first detection of the fatal neurological disease in a wild deer in this county, and this deer was found nearly 100 miles from the state’s primary CWD area near Preston, Minnesota.
“An informed citizen did the right thing by calling DNR, which allowed us to identify and remove this deer from the landscape,” said Lou Cornicelli, DNR wildlife research manager. “We’re hopeful the disease is not widespread in the area.”
In the short term, the DNR is developing plans to sample deer opportunistically until the fall hunting season. Cornicelli said deer hunting is the primary tool for managing this disease and the DNR will follow its CWD response plan PDFto identify a CWD management zone that will be at least 15 miles around the positive deer.
Hunters can expect to see carcass movement restrictions and mandatory surveillance. People who are unfamiliar with how deer are managed in Minnesota can find deer-related information, including hunting, natural history of deer and the state’s deer management plan, on the DNR deer management webpage. The DNR will work closely with tribal communities and with cities, townships and counties to manage this disease collaboratively.
In addition, the DNR will prohibit recreational deer feeding. Until then, the DNR asks that residents voluntarily stop feeding deer.
The Board of Animal Health, which oversees farmed deer and elk in the state, is expanding its endemic area for CWD based on this new detection by the DNR. The Board establishes the endemic area boundary 15 miles around all confirmed cases of CWD in the wild.
Additional CWD information
CWD affects the cervid family, which includes deer, elk and moose. The disease is not known to affect human or pet health. It is spread through direct contact with an infected deer’s saliva, urine, blood, feces, antler velvet or carcass. There is no vaccine or treatment for this disease.
For more information on chronic wasting disease, including maps of CWD surveillance areas, frequently asked questions and hunter information, visit mndnr.gov/cwd.
Discovery marks first case of CWD in this area of Minnesota
A wild deer in Dakota County was confirmed positive for chronic wasting disease, the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources said.
The deer, an adult male, was reported by a local resident near Farmington as displaying neurological symptoms and was tested as part of the DNR’s risk-based disease surveillance program.
It is the first detection of the fatal neurological disease in a wild deer in this county, and this deer was found nearly 100 miles from the state’s primary CWD area near Preston, Minnesota.
“An informed citizen did the right thing by calling DNR, which allowed us to identify and remove this deer from the landscape,” said Lou Cornicelli, DNR wildlife research manager. “We’re hopeful the disease is not widespread in the area.”
In the short term, the DNR is developing plans to sample deer opportunistically until the fall hunting season. Cornicelli said deer hunting is the primary tool for managing this disease and the DNR will follow its CWD response plan PDFto identify a CWD management zone that will be at least 15 miles around the positive deer.
Hunters can expect to see carcass movement restrictions and mandatory surveillance. People who are unfamiliar with how deer are managed in Minnesota can find deer-related information, including hunting, natural history of deer and the state’s deer management plan, on the DNR deer management webpage. The DNR will work closely with tribal communities and with cities, townships and counties to manage this disease collaboratively.
In addition, the DNR will prohibit recreational deer feeding. Until then, the DNR asks that residents voluntarily stop feeding deer.
The Board of Animal Health, which oversees farmed deer and elk in the state, is expanding its endemic area for CWD based on this new detection by the DNR. The Board establishes the endemic area boundary 15 miles around all confirmed cases of CWD in the wild.
Additional CWD information
CWD affects the cervid family, which includes deer, elk and moose. The disease is not known to affect human or pet health. It is spread through direct contact with an infected deer’s saliva, urine, blood, feces, antler velvet or carcass. There is no vaccine or treatment for this disease.
For more information on chronic wasting disease, including maps of CWD surveillance areas, frequently asked questions and hunter information, visit mndnr.gov/cwd.
South metro CWD
A wild deer in Dakota County has been identified as positive for chronic wasting disease. Here’s what we know.
Discovery
 A resident near Farmington contacted DNR to report an adult male deer on their property that was displaying neurological symptoms such as being unafraid of humans, stumbling, swaying and moving with its head hanging low.
A resident near Farmington contacted DNR to report an adult male deer on their property that was displaying neurological symptoms such as being unafraid of humans, stumbling, swaying and moving with its head hanging low.
A DNR conservation officer dispatched the deer and it was tested for CWD as part of DNR’s risk-based surveillance program.
This is the first detection of the fatal neurological disease in a wild deer in this county and is nearly 100 miles from DNR’s primary CWD area near Preston, Minnesota.
Deer feeding bans
In the future, the DNR plans to prohibit recreational deer feeding, similarly to other areas of the state. For now, the DNR asks that residents voluntarily stop feeding deer.
Next steps
- The DNR is currently developing plans to sample deer opportunistically until the fall hunting season.
- The DNR will work to identify a CWD management zone that will be at least 15 miles around the positive deer, in accordance to its CWD response plan.
- This fall, hunters can expect to see carcass movement restrictions and mandatory surveillance.
- People who are unfamiliar with deer management are encouraged to spend some time on the DNR's deer management page.
SATURDAY, MARCH 14, 2020
Minnesota 4 More Farmed Deer and 1 wild positive for CWD TSE Prion
FRIDAY, JANUARY 10, 2020
Minnesota Investigation leads to additional CWD positive deer on Pine County farm
TUESDAY, JANUARY 21, 2020
Minnesota CWD update test results from deer harvested in the 2019 hunting season and the special hunts have returned 27 wild deer tested positive for CWD all from the southeast DMZ
MONDAY, FEBRUARY 24, 2020
Minnesota New deer feeding bans in effect as part of CWD prevention efforts February 24, 2020
Taypayers paid more than $500,000 for deer farm buyouts the last three years $129,000 in Minnesota last year eclipsed prior two years combined.
By Tony Kennedy Star Tribune MARCH 12, 2020 — 11:07AM TEXT SIZE EMAIL PRINT MORE
American taxpayers gave a total of more than $510,000 to deer farmers in Minnesota and Wisconsin to wipe out captive herds infected with chronic wasting disease (CWD) in 2017, 2018 and 2019, according to records released by the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
The expense increased each year, growing to $270,956 last year. The Star Tribune obtained the payment data under the Freedom of Information Act, but the USDA declined to detail the cases or identify who received the money.
According to the data, Minnesota deer farmers received $93,616 in 2017, $20,195 in 2018 and $128,926 last year — the largest sum for either state in the three-year period. Deer farms in Wisconsin collected a total of $270,115 under the federal indemnity program for captive deer and elk over the same three years, records show. (There were no buyouts in Wisconsin in 2017.)
Former deer farmer Bruce Hoseck of Winona, Minn., declined to say how much money he received from the USDA in exchange for depopulating his herd in 2018. CWD was discovered inside his enclosure during mandated testing of a deceased 3-year-old buck in November 2017. In December of that year, a second deer carcass at the farm tested positive for the disease.
Hoseck said he joined the USDA’s livestock indemnification program in 2018 at the urging of state officials and because he was nearing retirement. By accepting money from the agency, he agreed to have his small herd of white-tailed deer killed and tested for CWD. All seven deer remaining in Hoseck’s herd tested positive for the disease and the state Department of Natural Resources blamed Hoseck’s farm for spreading CWD to wild deer outside his fence.
Related story
Deer farms in Minnesota have emerged as a flash point in the testy debate over who is to blame for spreading the deadly chronic wasting disease to the state’s wild deer. Online at bit.ly/stribchronicwasting.
Hoseck said he was impressed with the USDA’s valuation process — assigning buyout values for each individual deer. Antler size and pedigree were two notable factors in the appraisals, he said.
“I was satisfied with what they offered,” Hoseck said. “There were no negotiations.”
John Zanmiller, a lobbyist and spokesman for Whitetail Blufflands Association, a deer hunting group in southeastern Minnesota, said the USDA herd buyout program for infected deer farms is “like a dose of nasty medicine.”
For management of CWD, he said, it’s critical to kill captive deer herds infected with the disease. But some hunters wonder why the expense falls to taxpayers, Zanmiller said.
“Where’s the deer farmer’s contribution?” Zanmiller asked. “The buyouts promote the idea of private wealth at public expense.”
He also questioned why the program lacks transparency. There can’t be public scrutiny of the payments as long as case details aren’t disclosed, he said.
Limited disclosure
The USDA cited privacy laws and legal constraints involving trade secrets in denying the release of additional information. In late July, the Star Tribune submitted a written request to the USDA for details on last year’s buyout of a large Crow Wing County deer herd first found to be infected with CWD in 2016. The newspaper also asked for a summary of how many deer farms in Minnesota and Wisconsin participated in the program dating back to 2000 and how much money was paid out to them.
The department’s reply, received last month, provided total disbursements in each state for 2017, 2018 and 2019. The reply also said $27,610 went to Wisconsin in 2015.
In a letter, the agency said it would disclose only a single page from 114 pages of records that it determined were responsive to the newspaper’s request. “We determined that it was appropriate to fully withhold 113 pages,” the USDA said.
Donna Karlsons, a USDA public affairs specialist, previously said that a limited budget is available for animal payments under the deer and elk herd buyout program for CWD control. The maximum payment is $3,000 per animal and the fiscal 2019 budget allocated $1.3 million for CWD indemnity, she said. Buyout requests are prioritized based on risk factors that vary by case, Karlsons said.
In the Crow Wing County case at Trophy Woods Ranch, USDA sharpshooters last April killed 89 deer, including seven that tested positive for CWD. Another 13 animals were found on the property, decomposed and unable to be tested. The Minnesota Board of Animal Health said that only one other deer from a separate Minnesota herd was euthanized in 2019. If the Crow Wing farm only got paid for the live deer that were killed and tested, the average payment per deer in Minnesota in 2019 would have been $1,432.
The payment data from the USDA included an entry of $4,472 paid to the city of Winona in 2018. No details were provided by the USDA, but Winona City Manager Steve Sarvi said the payment was for three captive deer in the city’s now-defunct Prairie Island deer park. The animals were euthanized under the indemnity program because state officials wanted them tested for CWD.
The three city-owned deer had possibly been exposed to CWD because they once lived on Hoseck’s farm. They did not test positive. Winona acquired the three female deer by trading a city-owned buck to Hoseck in April 2016. The trade was made to diversify genetics in the city’s herd. The USDA payment to Winona averaged $1,490 per deer.
The city closed its deer park last year, Sarvi said.
The taxpayer-funded herd buyouts to control CWD require participating deer farmers to disinfect equipment within their enclosures, burn all organic matter in the pens, and maintain fencing to keep wild deer from entering. For five years, the sites are posted as biohazard sites because they are believed to contain the infectious prions that CWD-infected animals shed through their saliva, feces, urine and antler velvet.
In Minnesota, 300 deer and elk farms are regulated by the Board of Animal Health. This year, the agency has twice used the USDA’s CWD-related indemnity program to kill and test eight whitetails on a Pine County deer farm and four deer on a Wadena County farm, the agency said.
Tony Kennedy is an outdoors writer covering Minnesota news about fishing, hunting, wildlife, conservation, camping, natural resource management, public land, forests and water.
tony.kennedy@startribune.com 612-673-4213 tonykennedy
Taypayers paid more than $500,000 for deer farm buyouts the last three years $129,000 in Minnesota last year eclipsed prior two years combined.
By Tony Kennedy Star Tribune MARCH 12, 2020 — 11:07AM
SUNDAY, FEBRUARY 09, 2020
Management of chronic wasting disease in ranched elk: conclusions from a longitudinal three-year study
Although the herd owners were presented with additional management directives, including culling of CWD positive bulls and those animals positive by an amplification assay (RT-QuIC), they were not implemented due to concern regarding its potential impact on hunting revenue.
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 25, 2020
***> Novel Strain of the Chronic Wasting Disease Agent Isolated From Experimentally Inoculated Elk With LL132 Prion Protein
Accurate Genomic Predictions for Chronic Wasting Disease in U.S. White-tailed Deer
Christopher M Seabury*1, David L Oldeschulte1, Eric K Bhattarai1, Dhruti Legare2, Pamela J
Ferro2, Richard P Metz3, Charles D Johnson3, Mitchell A. Lockwood4, Tracy A. Nichols5
Conclusions
Herein, we demonstrate that differential susceptibility to CWD and variation in natural disease progression are both heritable, polygenic traits in farmed U.S. WTD, and that genome-
wide SNP data can be used to produce accurate genomic predictions for risk (≥ 0.8167); thereby
providing the first novel strategy for reducing the prevalence of CWD.
***>Moreover, given the genomic architecture of these traits, we also demonstrate that PRNP genotyping alone cannot be expected to facilitate an eradication program, or to rapidly reduce the overall prevalence of CWD in farmed U.S. WTD.
CWD WEBINAR CWD YESTERDAY! December 11, 2019
Dr. Mckenzie and CIDRAP on CWD TSE Prion
122: Prions and Chronic Wasting Disease with Jason Bartz
Texas CWD Symposium: Transmission by Saliva, Feces, Urine & Blood
the other part, these tissues and things in the body then shed or secrete prions which then are the route to other animals into the environment, so in particular, the things, the secretions that are infectious are salvia, feces, blood and urine. so pretty much anything that comes out of a deer is going to be infectious and potential for transmitting disease.
''On January 21, 2017 a tornado took down thousands of feet of fence for a 420-acre illegal deer enclosure in Lamar County that had been subject to federal and state investigation for illegally importing white-tailed deer into Mississippi from Texas (a CWD positive state). Native deer were free to move on and off the property before all of the deer were able to be tested for CWD. Testing will be made available for a period of three years for CWD on the property and will be available for deer killed within a 5-mile radius of the property on a voluntary basis. ''
Texas Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion Symposium 2018 posted January 2019 VIDEO SET 18 CLIPS
See Wisconsin update...terrible news, right after Texas updated map around 5 minute mark...
WISCONSIN CWD CAPTIVE CWD UPDATE VIDEO
cwd update on Wisconsin from Tammy Ryan...
Wyoming CWD Dr. Mary Wood
''first step is admitting you have a problem''
''Wyoming was behind the curve''
wyoming has a problem...
TEXAS BREEDER DEER ESCAPEE WITH CWD IN THE WILD, or so the genetics would show?
OH NO, please tell me i heard this wrong, a potential Texas captive escapee with cwd in the wild, in an area with positive captive cwd herd?
apparently, no ID though. tell me it ain't so please...
23:00 minute mark
''Free Ranging Deer, Dr. Deyoung looked at Genetics of this free ranging deer and what he found was, that the genetics on this deer were more similar to captive deer, than the free ranging population, but he did not see a significant connection to any one captive facility that he analyzed, so we believe, Ahhhhhh, this animal had some captive ahhh, whatnot.''
Wyoming CWD Dr. Mary Wood
''first step is admitting you have a problem''
''Wyoming was behind the curve''
wyoming has a problem...
the other part, these tissues and things in the body then shed or secrete prions which then are the route to other animals into the environment, so in particular, the things, the secretions that are infectious are salvia, feces, blood and urine. so pretty much anything that comes out of a deer is going to be infectious and potential for transmitting disease.
Texas Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion Symposium 2018 posted January 2019 VIDEO SET 18 CLIPS See Wisconsin update...terrible news, right after Texas updated map around 5 minute mark...
SATURDAY, JANUARY 19, 2019
Texas Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion Symposium 2018 posted January 2019 VIDEO SET 18 CLIPS
*** TEXAS TAHC OLD STATISTICS BELOW FOR PAST CWD TESTING ***
CWD TEXAS TAHC OLD FILE HISTORY
updated from some of my old files, some of the links will not work.
*** Subject: CWD testing in Texas ***
Date: Sun, 25 Aug 2002 19:45:14 –0500
From: Kenneth Waldrup
To: flounder@wt.net
snip...see ;
MONDAY, AUGUST 14, 2017
*** Texas Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion History ***
SUNDAY, MARCH 08, 2020
Texas CWD TSE Prion Confirms 169 Positive To Date
2020 Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy TSE Prion
***> 2020 CWD TSE PRION UPDATE GLOBAL MAP 2020
CWD TSE PRION UPDATE GLOBAL MAP 2020
SUNDAY, APRIL 12, 2020
PENNSYLVANIA REVISED CWD RESPONSE PLAN DRAFT AVAILABLE FOR REVIEW
FRIDAY, MARCH 06, 2020
Pennsylvania CWD TSE Prion deer and State Rep. David Maloney, R-Berks
THURSDAY, MARCH 05, 2020
PGC Audit Reeks of Politics Research Representative Maloney Wants To Gut wildlife management and hunting and help spread CWD in Pennsylvania
WEDNESDAY, MARCH 04, 2020
Politicians State Rep. David Maloney, R-Berks Helping to Spread Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion
just out!
WEDNESDAY, MARCH 04, 2020
Shedding and stability of CWD prion seeding activity in cervid feces
WEDNESDAY, MARCH 04, 2020
Pennsylvania YOUR STATE WILDLIFE AGENCY 2019 ANNUAL REPORT CWD TSE Prion 123 tested positive
March 2019
Pennsylvania Scrapie Infected Sheep Goat Flock
WEDNESDAY, MARCH 04, 2020
Pennsylvania YOUR STATE WILDLIFE AGENCY 2019 ANNUAL REPORT CWD TSE Prion 123 tested positive
WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 29, 2020
Pennsylvania CWD TSE Prion 2019-20 hunting seasons as of January 14, 148 of the samples had tested positive for CWD in Wild Deer
FRIDAY, FEBRUARY 28, 2020
Virginia DGIF say 21 new cases of CWD TSE Prion confirmed in white-tailed deer in northwest Virginia throughout 2019
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 25, 2020
Pennsylvania Agriculture Secretary Announces Research Funding to Combat Chronic Wasting Disease in PA Deer and it's going to the dogs
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 25, 2020
Iowa Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion Cases Climb To 89 positive To Date in Wild Cervid
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 18, 2020
Michigan CWD TSE Prion Total Suspect Positive Deer Moves Up To 185 with total deer tested 80,342 to date
FRIDAY, MARCH 06, 2020
Michigan CWD Research Projects Funded by the DNR and MSU
MONDAY, JANUARY 27, 2020
Michigan CWD TSE Prion MDARD 3 positive white-tailed deer from a Newaygo County deer farm depopulation and quarantine efforts update?
TUESDAY, JANUARY 07, 2020
Michigan Total CWD TSE Prion Positive Suspect-Positive Deer Jump To 174 confirmed to date
TUESDAY, JANUARY 14, 2020
Michigan MDARD has confirmed chronic wasting disease (CWD) in 3 white-tailed deer from a Newaygo County deer farm
SATURDAY, JANUARY 25, 2020
Tennessee 2019-20 deer season 462 CWD TSE Prion Confirmed To Date
FRIDAY, JANUARY 24, 2020
Wyoming Game & Fish Discovers CWD-Positive Mule Deer in Pinedale, Discourages Feeding of Wildlife
''As of September 2019, CWD has been identified in 31 of 37 (84%) Wyoming mule deer herds, nine of 36 (25%) elk herds, and generally wherever white-tailed deer occur. Increasing prevalence and distribution of CWD has the potential to cause widespread and long-term negative impacts to Wyoming’s cervid populations. Prevalence of this disease in chronically infected Wyoming deer herds has exceeded 40%, with one elk herd exhibiting nearly 15% prevalence.''
''for the first time, there is clear evidence that CWD is adversely affecting the overall health and viability of some herds.''
FRIDAY, JANUARY 24, 2020
Arkansas Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion FY2020 211 Positive Cases as of January 17, 2020
SUNDAY, JANUARY 05, 2020
Arkansas Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion 2019 to 2020 Totals As Of December 3, 2019 399 Confirmed with more pending results
WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 29, 2020
Utah CWD TSE Prion Since July 1, 2019, the DWR confirmed 16 positive deer statewide Six of those, including Coal, were in the La Sal Unit, 59 test pending
TUESDAY, MARCH 03, 2020
North Dakota Eight deer taken during the 2019 deer gun season tested positive for chronic wasting disease CWD TSE Prion
FRIDAY, JANUARY 17, 2020
North Dakota 11 Positive Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion detected since Sept 1, 2019
MONDAY, FEBRUARY 24, 2020
Minnesota New deer feeding bans in effect as part of CWD prevention efforts February 24, 2020
TUESDAY, JANUARY 21, 2020
Minnesota CWD update test results from deer harvested in the 2019 hunting season and the special hunts have returned 27 wild deer tested positive for CWD all from the southeast DMZ
FRIDAY, JANUARY 10, 2020
Minnesota Investigation leads to additional CWD positive deer on Pine County farm
WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 05, 2020
Wisconsin CWD TSE Prion 2019 to date wild deer 1317 positive and Captive Farmed Livestock Cervid CWD update
THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 28, 2019
Wisconsin CWD TSE Prion Explodes To 1,048 Positive 2018-2019 With Total 5,234 Confirmed To Date
THURSDAY, JANUARY 23, 2020
Wisconsin Confirms CWD Detected In Marquette and Marathon County
WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 08, 2020
Wisconsin Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion Positives in Farm-raised Deer in 2019
The majority of the positives have come after 2013 when DATCP began letting some deer farms and hunting ranches continue operating after CWD was detected on their property.
TUESDAY, JANUARY 07, 2020
Oklahoma Farmed Elk Lincoln County CWD Depopulation 3 Positive Elk with 1 Additional Dead Trace Out Confirmed Positive
WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 05, 2020
Wisconsin CWD TSE Prion 2019 to date wild deer 1317 positive and Captive Farmed Livestock Cervid CWD update
THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 27, 2020
Texas Chronic Wasting Disease Discovered at Deer Breeding Facility in Kimble County AND TO DATE, 169 postive cases detected white-tailed deer, red deer and mule deer
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 04, 2020
TEXAS REPORTS 20 NEW CWD TSE PRION CASES 3 WILD 17 BREEDER 166 POSITIVE TO DATE
THURSDAY, DECEMBER 19, 2019
TEXAS Val Verde County White-tailed Deer Tests Positive for Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion State Positive NOW at 147 Confirmed
FRIDAY, DECEMBER 20, 2019
Texas TAHC, Administrative Code, Title 4, Part 2, Chapter 40, Chronic Wasting Disease Amendments Open For Comment beginning December 20, 2019 thru January 20, 2020 Terry Singeltary Comments Submission
FRIDAY, DECEMBER 20, 2019
TEXAS ANIMAL HEALTH COMMISSION EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR ORDER DECLARING A CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE HIGH RISK AREA CONTAINMENT ZONE FOR PORTIONS OF VAL VERDE COUNTY
TUESDAY, DECEMBER 31, 2019
In Vitro detection of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) prions in semen and reproductive tissues of white tailed deer bucks (Odocoileus virginianus
SUNDAY, AUGUST 02, 2015
TEXAS CWD, Have you been ThunderStruck, deer semen, straw bred bucks, super ovulation, and the potential TSE Prion connection, what if?
SUNDAY, FEBRUARY 16, 2020
***> Jerking for Dollars, Are Texas Politicians and Legislators Masturbating Deer For Money, and likely spreading CWD TSE Prion?
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 11, 2020
South Dakota Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion Detected in New Areas
TUESDAY, JANUARY 28, 2020
Mississippi MDWFP North MS CWD Management Zone Since October 2019, 25 CWD-positive deer have been detected from this zone
SATURDAY, JANUARY 04, 2020
Mississippi CWD TOTALS JUST ABOUT DOUBLE Since October 1, 2019 To Date Statewide Total is 37 Confirmed
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 11, 2020
Missouri MDC 2019-2020 SAMPLING RESULTS CWD TSE PRION TO DATE 28 Positive
SUNDAY, JANUARY 19, 2020
Missouri CWD TSE Prion 2019-2020 SAMPLING RESULTS TO DATE 25 Positive
THURSDAY, JANUARY 02, 2020
Missouri MDC officially reports more than 20 new cases of Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion
FRIDAY, JANUARY 17, 2020
Montana Moose Tests Positive for Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE PRION in Libby Area
Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks 2019 CWD Surveillance Hunter Test Results CWD TSE PRION LOOKS LIKE 136 POSITIVE SO FAR, count them up...
WEDNESDAY, DECEMBER 25, 2019
Montana 16 more deer positive for CWD first time positive hunting district 705 in southeast
SUNDAY, DECEMBER 22, 2019
Illinois CWD TSE Prion 90 CWD-positive deer with 826 confirmed positive Total positives through June 30, 2019
THURSDAY, JANUARY 23, 2020
Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) has updated the following chapter of the Accredited Veterinarian's Manual: Chapter 13 Chronic Wasting Disease Herd Certification Programs
TUESDAY, JANUARY 21, 2020
2004 European Commission Chronic wasting disease AND TISSUES THAT MIGHT CARRY A RISK FOR HUMAN FOOD AND ANIMAL FEED CHAINS REPORT UPDATED 2020
THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 27, 2020
Michigan 65 CWD positive deer were identified from the 2019 hunting seasons
MONDAY, FEBRUARY 24, 2020
Michigan Deer processing plant quarantined and closed by inspectors rotting carcasses of approximately 13 deer in the freezer complaint came from Newaygo County
MONDAY, JANUARY 27, 2020
updated
Michigan CWD TSE Prion MDARD 3 positive white-tailed deer from a Newaygo County deer farm depopulation and quarantine efforts update?
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 18, 2020
Michigan CWD TSE Prion Total Suspect Positive Deer Moves Up To 185 with total deer tested 80,342 to date
THURSDAY, JANUARY 30, 2020
Michigan CWD TSE Prion Total Suspect Positive Deer Jumps To 181 to date
THURSDAY, DECEMBER 19, 2019
TSE surveillance statistics exotic species and domestic cats Update December 2019
THURSDAY, DECEMBER 19, 2019
The emergence of classical BSE from atypical/Nor98 scrapie
FRIDAY, DECEMBER 06, 2019
Estimating relative CWD susceptibility and disease progression in farmed white-tailed deer with rare PRNP alleles
WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 20, 2019
Review: Update on Classical and Atypical Scrapie in Sheep and Goats
WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 20, 2019
Sheep Are Susceptible to the Bovine Adapted Transmissible Mink Encephalopathy agent by Intracranial Inoculation and Have Evidence of Infectivity in Lymphoid Tissues
***> ''indicating that sheep inoculated with the bovine TME agent harbor infectivity in their lymph nodes despite a lack of detection with conventional immunoassays.''
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 11, 2020
Predators, Scavengers, and trans locating the CWD TSE Prion
FRIDAY, NOVEMBER 15, 2019
Southwest Wisconsin CWD, Deer and Predator Study
FRIDAY, NOVEMBER 08, 2019
EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ) Update on chronic wasting disease (CWD) III
WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 16, 2019
Australia Assessment of bulk wheat from Canada Part B: Animal biosecurity risk advice, CWD TSE Prion concerns are mounting
FRIDAY, MAY 24, 2019
Assessing chronic wasting disease strain differences in free-ranging cervids across the United States
TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 04, 2020
Predicting the spread-risk potential of chronic wasting disease to sympatric ungulate species
MONDAY, MAY 20, 2019
APHIS, USDA, Announces the Finalized Chronic Wasting Disease Herd Certification Program Standards Singeltary Submissions
SUNDAY, JANUARY 12, 2020 2019
USAHA-AAVLD Annual Meeting October 24-30, 2019 Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy TSE Prion CWD, Scrapie UPDATE
MONDAY, OCTOBER 07, 2019
Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) and Government Response Congressional Research Service May 17, 2019
WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 02, 2019
Chronic Wasting Disease In Cervids: Prevalence, Impact And Management Strategies
WEDNESDAY, JUNE 26, 2019
Subcommittee Hearing: Chronic Wasting Disease: The Threats to Wildlife, Public Lands, Hunting, and Health
video
CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE CONGRESS Serial No. 107-117 May 16, 2002
CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE
JOINT OVERSIGHT HEARING BEFORE THE SUBCOMMITTEE ON FORESTS AND FOREST HEALTH JOINT WITH THE SUBCOMMITTEE ON FISHERIES CONSERVATION, WILDLIFE AND OCEANS OF THE COMMITTEE ON RESOURCES U.S. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES ONE HUNDRED SEVENTH CONGRESS SECOND SESSION
May 16, 2002
Serial No. 107-117
snip...
Mr. MCINNIS. Today, this joint Subcommittee hearing will explore an issue of immeasurable importance to the growing number of communities in wide-ranging parts of this country, the growing incidence of Chronic Wasting Disease in North America’s wild and captive deer and elk populations. In a matter of just a few months, this once parochial concern has grown into something much larger and much more insidious than anyone could have imagined or predicted.
As each day passes, this problem grows in its size, scope, and consequence. One thing becomes clear. Chronic Wasting Disease is not a Colorado problem. It is a Wisconsin problem or a Nebraska or Wyoming problem. It is a national problem and anything short of a fully integrated, systematic national assault on this simply will not do, which is precisely why we brought our group together here today.
snip...
So this is a disease that is spreading throughout the continent and it is going to require a national response as well as the efforts that are currently taking place in States like Wisconsin, Colorado, Nebraska, Wyoming, the interest they now have down in Texas and some of the neighboring States that have large white-tailed deer population and also elk.
This is a huge issue for us, Mr. Chairman, in the State of Wisconsin. I want to commend Governor McCallum and your staff and the various agencies for the rapid response that you have shown, given the early detection of CWD after the last deer hunting season. The problem that we have, though, is just a lack of information, good science in regards to what is the best response, how dangerous is this disease. We cannot close the door, quite frankly, with the paucity of scientific research that is out there right now in regards to how the disease spreads, the exposure of other livestock herds—given the importance of our dairy industry in the State, that is a big issue—and also the human health effects.
FRIDAY, OCTOBER 04, 2019
Inactivation of chronic wasting disease prions using sodium hypochlorite
i think some hunters that don't read this carefully are going to think this is a cure all for cwd tse contamination. IT'S NOT!
first off, it would take a strong bleach type sodium hypochlorite, that is NOT your moms bleach she uses in her clothes, and store bought stuff.
Concentrated bleach is an 8.25 percent solution of sodium hypochlorite, up from the “regular bleach” concentration of 5.25 percent.Nov 1, 2013 https://waterandhealth.org/disinfect/high-strength-bleach-2/
second off, the study states plainly;
''We found that a five-minute treatment with a 40% dilution of household bleach was effective at inactivating CWD seeding activity from stainless-steel wires and CWD-infected brain homogenates. However, bleach was not able to inactivate CWD seeding activity from solid tissues in our studies.''
''We initially tested brains from two CWD-infected mice and one uninfected mouse using 40% bleach for 5 minutes. The results from these experiments showed almost no elimination of prion seeding activity (Table 4). We then increased the treatment time to 30 minutes and tested 40% and 100% bleach treatments. Again, the results were disappointing and showed less than a 10-fold decrease in CWD-seeding activity (Table 4). Clearly, bleach is not able to inactivate prions effectively from small brain pieces under the conditions tested here.''
''We found that both the concentration of bleach and the time of treatment are critical for inactivation of CWD prions. A 40% bleach treatment for 5 minutes successfully eliminated detectable prion seeding activity from both CWD-positive brain homogenate and stainless-steel wires bound with CWD. However, even small solid pieces of CWD-infected brain were not successfully decontaminated with the use of bleach.''
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0223659
https://chronic-wasting-disease.blogspot.com/2019/10/inactivation-of-chronic-wasting-disease.html
i think with all the fear from recent studies, and there are many, of potential, or likelihood of zoonosis, if it has not already happened as scjd, i think this study came out to help out on some of that fear, that maybe something will help, but the study plainly states it's for sure not a cure all for exposure and contamination of the cwd tse prion on surface materials. imo...terry
HUNTERS, CWD TSE PRION, THIS SHOULD A WAKE UP CALL TO ALL OF YOU GUTTING AND BONING OUT YOUR KILL IN THE FIELD, AND YOUR TOOLS YOU USE...
* 1: J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1994 Jun;57(6):757-8
Transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease to a chimpanzee by electrodes contaminated during neurosurgery.
Gibbs CJ Jr, Asher DM, Kobrine A, Amyx HL, Sulima MP, Gajdusek DC.
Laboratory of Central Nervous System Studies, National Institute of
Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health,
Bethesda, MD 20892.
Stereotactic multicontact electrodes used to probe the cerebral cortex of a middle aged woman with progressive dementia were previously implicated in the accidental transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) to two younger patients. The diagnoses of CJD have been confirmed for all three cases. More than two years after their last use in humans, after three cleanings and repeated sterilisation in ethanol and formaldehyde vapour, the electrodes were implanted in the cortex of a chimpanzee. Eighteen months later the animal became ill with CJD. This finding serves to re-emphasise the potential danger posed by reuse of instruments contaminated with the agents of spongiform encephalopathies, even after scrupulous attempts to clean them.
PMID: 8006664 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Wednesday, September 11, 2019
Is the re-use of sterilized implant abutments safe enough? (Implant abutment safety) iatrogenic TSE Prion
172. Establishment of PrPCWD extraction and detection methods in the farm soil
Kyung Je Park, Hoo Chang Park, In Soon Roh, Hyo Jin Kim, Hae-Eun Kang and Hyun Joo Sohn
Foreign Animal Disease Division, Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Gimcheon, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Korea
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) is a fatal neurodegenerative disorder, which is so-called as prion diseases due to the causative agents (PrPSc). TSEs are believed to be due to the template-directed accumulation of disease-associated prion protein, generally designated PrPSc. Chronic wasting disease (CWD) is the prion disease that is known spread horizontally. CWD has confirmed last in Republic of Korea in 2016 since first outbreak of CWD in 2001. The environmental reservoirs mediate the transmission of this disease. The significant levels of infectivity have been detected in the saliva, urine, and faeces of TSE-infected animals. Soil can serve as a stable reservoir for infectious prion proteins. We found that PrPCWD can be extracted and detected in CWD contaminated soil which has kept at room temperature until 4 years after 0.001 ~ 1% CWD exposure and natural CWD-affected farm soil through PBS washing and sPMCAb.
Materials and Methods: Procedure of serial PMCAb. CWD contaminated soil which has kept at room temperature (RT) for 1 ~ 4 year after 0.001%~1% CWD brain homogenates exposure for 4 months collected 0.14 g. The soil was collected by the same method once of year until 4 year after stop CWD exposure. We had conducted the two steps. There are two kinds of 10 times washing step and one amplification step. The washing step was detached PrPSc from contaminated soil by strong vortex with maximum rpm. We harvest supernatant every time by 10 times. As the other washing step, the Washed soil was made by washing 10 times soil using slow rotator and then harvest resuspended PBS for removing large impurity material. Last step was prion amplification step for detection of PrPCWD in soil supernatant and the washed soil by sPMCAb. Normal brain homogenate (NBH) was prepared by homogenization of brains with glass dounce in 9 volumes of cold PBS with TritonX-100, 5 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl and 0.05% Digitonin (sigma) plus Complete mini protease inhibitors (Roche) to a final concentration of 5%(w/v) NBHs were centrifuged at 2000 g for 1 min, and supernatant removed and frozen at −70 C for use. CWD consisted of brain from natural case in Korea and was prepared as 10%(w/v) homogenate. Positive sample was diluted to a final dilution 1:1000 in NBH, with serial 3:7 dilutions in NBH. Sonication was performed with a Misonix 4000 sonicator with amplitude set to level 70, generating an average output of 160W with two teflon beads during each cycle. One round consisted of 56 cycles of 30 s of sonication followed 9 min 30 s of 37°C incubation. Western Blotting (WB) for PrPSc detection. The samples (20 µL) after each round of amplification were mixed with proteinase K (2 mg/ml) and incubated 37°C for 1 h. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membrane. After blocking, the membrane was incubated for 1 h with 1st antibody S1 anti rabbit serum (APQA, 1:3000) and developed with enhanced chemiluminescence detection system.
Results: We excluded from first to third supernatant in view of sample contamination. It was confirmed abnormal PrP amplification in all soil supernatants from fourth to tenth. From 0.01% to 1% contaminated washed soils were identified as abnormal prions. 0.001% contaminated washed soil did not show PrP specific band (Fig 1). The soil was collected by the same method once of year until 4 year after stop CWD exposure. After sPMCAb, there were no PrPCWD band in from second to fourth year 0.001% washed soil. but It was confirmed that the abnormal prion was amplified in the washing supernatant which was not amplified in the washed soil. we have decided to use soil supernatant for soil testing (Fig. 2). After third rounds of amplification, PrPSc signals observed in three out of four sites from CWD positive farm playground. No signals were observed in all soil samples from four CWD negative farm (Fig. 3).
Conclusions: Our studies showed that PrPCWD persist in 0.001% CWD contaminated soil for at least 4 year and natural CWD-affected farm soil. When cervid reintroduced into CWD outbreak farm, the strict decontamination procedures of the infectious agent should be performed in the environment of CWD-affected cervid habitat.
===
186. Serial detection of hematogenous prions in CWD-infected deer
Amy V. Nalls, Erin E. McNulty, Nathaniel D. Denkers, Edward A. Hoover and Candace K. Mathiason
Department of Microbiology, Immunology, and Pathology, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA
CONTACT Amy V. Nalls amy.nalls@colostate.edu
ABSTRACT
Blood contains the infectious agent associated with prion disease affecting several mammalian species, including humans, cervids, sheep, and cattle. It has been confirmed that sufficient prion agent is present in the blood of both symptomatic and asymptomatic carriers to initiate the amyloid templating and accumulation process that results in this fatal neurodegenerative disease. Yet, to date, the ability to detect blood-borne prions by in vitro methods remains difficult.
We have capitalized on blood samples collected from longitudinal chronic wasting disease (CWD) studies in the native white-tailed deer host to examine hematogenous prion load in blood collected minutes, days, weeks and months post exposure. Our work has focused on refinement of the amplification methods RT-QuIC and PMCA. We demonstrate enhanced in vitro detection of amyloid seeding activity (prions) in blood cell fractions harvested from deer orally-exposed to 300 ng CWD positive brain or saliva.
These findings permit assessment of the role hematogenous prions play in the pathogenesis of CWD and provide tools to assess the same for prion diseases of other mammalian species.
Considering the oral secretion of prions, saliva from CWD-infected deer was shown to transmit disease to other susceptible naïve deer when harvested from the animals in both the
and preclinical stages69
of infection, albeit within relatively large volumes of saliva (50 ml). In sheep with preclinical, natural scrapie infections, sPMCA facilitated the detection of PrPSc within buccal swabs throughout most of the incubation period of the disease with an apparent peak in prion secretion around the mid-term of disease progression.70
The amounts of prion present in saliva are likely to be low as indicated by CWD-infected saliva producing prolonged incubation periods and incomplete attack rates within the transgenic mouse bioassay.41
snip...
Indeed, it has also been shown that the scrapie and CWD prions are excreted in urine, feces and saliva and are likely to be excreted from skin. While levels of prion within these excreta/secreta are very low, they are produced throughout long periods of preclinical disease as well as clinical disease. Furthermore, the levels of prion in such materials are likely to be increased by concurrent inflammatory conditions affecting the relevant secretory organ or site. Such dissemination of prion into the environment is very likely to facilitate the repeat exposure of flockmates to low levels of the disease agent, possibly over years.
snip...
Given the results with scrapie-contaminated milk and CWD-contaminated saliva, it seems very likely that these low levels of prion in different secreta/excreta are capable of transmitting disease upon prolonged exposure, either through direct animal-to-animal contact or through environmental reservoirs of infectivity.
the other part, these tissues and things in the body then shed or secrete prions which then are the route to other animals into the environment, so in particular, the things, the secretions that are infectious are salvia, feces, blood and urine. so pretty much anything that comes out of a deer is going to be infectious and potential for transmitting disease.
***>>> Recently, we have been using PMCA to study the role of environmental prion contamination on the horizontal spreading of TSEs. These experiments have focused on the study of the interaction of prions with plants and environmentally relevant surfaces. Our results show that plants (both leaves and roots) bind tightly to prions present in brain extracts and excreta (urine and feces) and retain even small quantities of PrPSc for long periods of time. Strikingly, ingestion of prioncontaminated leaves and roots produced disease with a 100% attack rate and an incubation period not substantially longer than feeding animals directly with scrapie brain homogenate. Furthermore, plants can uptake prions from contaminated soil and transport them to different parts of the plant tissue (stem and leaves). Similarly, prions bind tightly to a variety of environmentally relevant surfaces, including stones, wood, metals, plastic, glass, cement, etc. Prion contaminated surfaces efficiently transmit prion disease when these materials were directly injected into the brain of animals and strikingly when the contaminated surfaces were just placed in the animal cage. These findings demonstrate that environmental materials can efficiently bind infectious prions and act as carriers of infectivity, suggesting that they may play an important role in the horizontal transmission of the disease.
========================
Since its invention 13 years ago, PMCA has helped to answer fundamental questions of prion propagation and has broad applications in research areas including the food industry, blood bank safety and human and veterinary disease diagnosis.
HUNTERS, CWD TSE PRION, THIS SHOULD A WAKE UP CALL TO ALL OF YOU GUTTING AND BONING OUT YOUR KILL IN THE FIELD, AND YOUR TOOLS YOU USE...
* 1: J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1994 Jun;57(6):757-8
Transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease to a chimpanzee by electrodes contaminated during neurosurgery.
Gibbs CJ Jr, Asher DM, Kobrine A, Amyx HL, Sulima MP, Gajdusek DC.
Laboratory of Central Nervous System Studies, National Institute of
Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health,
Bethesda, MD 20892.
Stereotactic multicontact electrodes used to probe the cerebral cortex of a middle aged woman with progressive dementia were previously implicated in the accidental transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) to two younger patients. The diagnoses of CJD have been confirmed for all three cases. More than two years after their last use in humans, after three cleanings and repeated sterilisation in ethanol and formaldehyde vapour, the electrodes were implanted in the cortex of a chimpanzee. Eighteen months later the animal became ill with CJD. This finding serves to re-emphasise the potential danger posed by reuse of instruments contaminated with the agents of spongiform encephalopathies, even after scrupulous attempts to clean them.
PMID: 8006664 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Wednesday, September 11, 2019
Is the re-use of sterilized implant abutments safe enough? (Implant abutment safety) iatrogenic TSE Prion
SATURDAY, MARCH 16, 2019
Medical Devices Containing Materials Derived from Animal Sources (Except for In Vitro Diagnostic Devices) Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff Document issued on March 15, 2019 Singeltary Submission
THURSDAY, SEPTEMBER 27, 2018
***> Estimating the impact on food and edible materials of changing scrapie control measures: The scrapie control model
THE tse prion aka mad cow type disease is not your normal pathogen.
The TSE prion disease survives ashing to 600 degrees celsius, that’s around 1112 degrees farenheit.
you cannot cook the TSE prion disease out of meat.
you can take the ash and mix it with saline and inject that ash into a mouse, and the mouse will go down with TSE.
Prion Infected Meat-and-Bone Meal Is Still Infectious after Biodiesel Production as well.
the TSE prion agent also survives Simulated Wastewater Treatment Processes.
IN fact, you should also know that the TSE Prion agent will survive in the environment for years, if not decades.
you can bury it and it will not go away.
The TSE agent is capable of infected your water table i.e. Detection of protease-resistant cervid prion protein in water from a CWD-endemic area.
it’s not your ordinary pathogen you can just cook it out and be done with.
***> that’s what’s so worrisome about Iatrogenic mode of transmission, a simple autoclave will not kill this TSE prion agent.
1: J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1994 Jun;57(6):757-8
***> Transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease to a chimpanzee by electrodes contaminated during neurosurgery.
Gibbs CJ Jr, Asher DM, Kobrine A, Amyx HL, Sulima MP, Gajdusek DC.
Laboratory of Central Nervous System Studies, National Institute of
Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health,
Bethesda, MD 20892.
Stereotactic multicontact electrodes used to probe the cerebral cortex of a middle aged woman with progressive dementia were previously implicated in the accidental transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) to two younger patients. The diagnoses of CJD have been confirmed for all three cases. More than two years after their last use in humans, after three cleanings and repeated sterilisation in ethanol and formaldehyde vapour, the electrodes were implanted in the cortex of a chimpanzee. Eighteen months later the animal became ill with CJD. This finding serves to re-emphasise the potential danger posed by reuse of instruments contaminated with the agents of spongiform encephalopathies, even after scrupulous attempts to clean them.
PMID: 8006664 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
2018 - 2019
***> This is very likely to have parallels with control efforts for CWD in cervids.
Rapid recontamination of a farm building occurs after attempted prion removal
Kevin Christopher Gough, BSc (Hons), PhD1, Claire Alison Baker, BSc (Hons)2, Steve Hawkins, MIBiol3, Hugh Simmons, BVSc, MRCVS, MBA, MA3, Timm Konold, DrMedVet, PhD, MRCVS3 and Ben Charles Maddison, BSc (Hons), PhD2
Abstract
The transmissible spongiform encephalopathy scrapie of sheep/goats and chronic wasting disease of cervids are associated with environmental reservoirs of infectivity.
Preventing environmental prions acting as a source of infectivity to healthy animals is of major concern to farms that have had outbreaks of scrapie and also to the health management of wild and farmed cervids.
Here, an efficient scrapie decontamination protocol was applied to a farm with high levels of environmental contamination with the scrapie agent.
Post-decontamination, no prion material was detected within samples taken from the farm buildings as determined using a sensitive in vitro replication assay (sPMCA).
A bioassay consisting of 25 newborn lambs of highly susceptible prion protein genotype VRQ/VRQ introduced into this decontaminated barn was carried out in addition to sampling and analysis of dust samples that were collected during the bioassay.
Twenty-four of the animals examined by immunohistochemical analysis of lymphatic tissues were scrapie-positive during the bioassay, samples of dust collected within the barn were positive by month 3.
The data illustrates the difficulty in decontaminating farm buildings from scrapie, and demonstrates the likely contribution of farm dust to the recontamination of these environments to levels that are capable of causing disease.
snip...
As in the authors' previous study,12 the decontamination of this sheep barn was not effective at removing scrapie infectivity, and despite the extra measures brought into this study (more effective chemical treatment and removal of sources of dust) the overall rates of disease transmission mirror previous results on this farm. With such apparently effective decontamination (assuming that at least some sPMCA seeding ability is coincident with infectivity), how was infectivity able to persist within the environment and where does infectivity reside? Dust samples were collected in both the bioassay barn and also a barn subject to the same decontamination regime within the same farm (but remaining unoccupied). Within both of these barns dust had accumulated for three months that was able to seed sPMCA, indicating the accumulation of scrapie-containing material that was independent of the presence of sheep that may have been incubating and possibly shedding low amounts of infectivity.
This study clearly demonstrates the difficulty in removing scrapie infectivity from the farm environment. Practical and effective prion decontamination methods are still urgently required for decontamination of scrapie infectivity from farms that have had cases of scrapie and this is particularly relevant for scrapiepositive goatherds, which currently have limited genetic resistance to scrapie within commercial breeds.24 This is very likely to have parallels with control efforts for CWD in cervids.
Acknowledgements The authors thank the APHA farm staff, Tony Duarte, Olly Roberts and Margaret Newlands for preparation of the sheep pens and animal husbandry during the study. The authors also thank the APHA pathology team for RAMALT and postmortem examination.
Funding This study was funded by DEFRA within project SE1865.
Competing interests None declared.
Saturday, January 5, 2019
Rapid recontamination of a farm building occurs after attempted prion removal
THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 28, 2019
BSE infectivity survives burial for five years with only limited spread
***> CONGRESSIONAL ABSTRACTS PRION CONFERENCE 2018
P69 Experimental transmission of CWD from white-tailed deer to co-housed reindeer
Mitchell G (1), Walther I (1), Staskevicius A (1), Soutyrine A (1), Balachandran A (1)
(1) National & OIE Reference Laboratory for Scrapie and CWD, Canadian Food Inspection Agency, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Chronic wasting disease (CWD) continues to be detected in wild and farmed cervid populations of North America, affecting predominantly white-tailed deer, mule deer and elk. Extensive herds of wild caribou exist in northern regions of Canada, although surveillance has not detected the presence of CWD in this population. Oral experimental transmission has demonstrated that reindeer, a species closely related to caribou, are susceptible to CWD. Recently, CWD was detected for the first time in Europe, in wild Norwegian reindeer, advancing the possibility that caribou in North America could also become infected. Given the potential overlap in habitat between wild CWD-infected cervids and wild caribou herds in Canada, we sought to investigate the horizontal transmissibility of CWD from white-tailed deer to reindeer.
Two white-tailed deer were orally inoculated with a brain homogenate prepared from a farmed Canadian white-tailed deer previously diagnosed with CWD. Two reindeer, with no history of exposure to CWD, were housed in the same enclosure as the white-tailed deer, 3.5 months after the deer were orally inoculated. The white-tailed deer developed clinical signs consistent with CWD beginning at 15.2 and 21 months post-inoculation (mpi), and were euthanized at 18.7 and 23.1 mpi, respectively. Confirmatory testing by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and western blot demonstrated widespread aggregates of pathological prion protein (PrPCWD) in the central nervous system and lymphoid tissues of both inoculated white-tailed deer. Both reindeer were subjected to recto-anal mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (RAMALT) biopsy at 20 months post-exposure (mpe) to the white-tailed deer. The biopsy from one reindeer contained PrPCWD confirmed by IHC. This reindeer displayed only subtle clinical evidence of disease prior to a rapid decline in condition requiring euthanasia at 22.5 mpe. Analysis of tissues from this reindeer by IHC revealed widespread PrPCWD deposition, predominantly in central nervous system and lymphoreticular tissues. Western blot molecular profiles were similar between both orally inoculated white-tailed deer and the CWD positive reindeer. Despite sharing the same enclosure, the other reindeer was RAMALT negative at 20 mpe, and PrPCWD was not detected in brainstem and lymphoid tissues following necropsy at 35 mpe. Sequencing of the prion protein gene from both reindeer revealed differences at several codons, which may have influenced susceptibility to infection.
Natural transmission of CWD occurs relatively efficiently amongst cervids, supporting the expanding geographic distribution of disease and the potential for transmission to previously naive populations. The efficient horizontal transmission of CWD from white-tailed deer to reindeer observed here highlights the potential for reindeer to become infected if exposed to other cervids or environments infected with CWD.
***> Infectious agent of sheep scrapie may persist in the environment for at least 16 years
***> Nine of these recurrences occurred 14–21 years after culling, apparently as the result of environmental contamination, but outside entry could not always be absolutely excluded.
Gudmundur Georgsson,1 Sigurdur Sigurdarson2 and Paul Brown3
Correspondence
Gudmundur Georgsson ggeorgs@hi.is
1 Institute for Experimental Pathology, University of Iceland, Keldur v/vesturlandsveg, IS-112 Reykjavı´k, Iceland
2 Laboratory of the Chief Veterinary Officer, Keldur, Iceland
3 Bethesda, Maryland, USA
Received 7 March 2006 Accepted 6 August 2006
In 1978, a rigorous programme was implemented to stop the spread of, and subsequently eradicate, sheep scrapie in Iceland. Affected flocks were culled, premises were disinfected and, after 2–3 years, restocked with lambs from scrapie-free areas. Between 1978 and 2004, scrapie recurred on 33 farms. Nine of these recurrences occurred 14–21 years after culling, apparently as the result of environmental contamination, but outside entry could not always be absolutely excluded. Of special interest was one farm with a small, completely self-contained flock where scrapie recurred 18 years after culling, 2 years after some lambs had been housed in an old sheephouse that had never been disinfected. Epidemiological investigation established with near certitude that the disease had not been introduced from the outside and it is concluded that the agent may have persisted in the old sheep-house for at least 16 years.
TITLE: PATHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE IN REINDEER AND DEMONSTRATION OF HORIZONTAL TRANSMISSION
*** DECEMBER 2016 CDC EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE JOURNAL CWD HORIZONTAL TRANSMISSION
SEE;
Back around 2000, 2001, or so, I was corresponding with officials abroad during the bse inquiry, passing info back and forth, and some officials from here inside USDA aphis FSIS et al. In fact helped me get into the USA 50 state emergency BSE conference call way back. That one was a doozy. But I always remember what “deep throat” I never knew who they were, but I never forgot;
Some unofficial information from a source on the inside looking out -
Confidential!!!!
As early as 1992-3 there had been long studies conducted on small pastures containing scrapie infected sheep at the sheep research station associated with the Neuropathogenesis Unit in Edinburgh, Scotland. Whether these are documented...I don't know. But personal recounts both heard and recorded in a daily journal indicate that leaving the pastures free and replacing the topsoil completely at least 2 feet of thickness each year for SEVEN years....and then when very clean (proven scrapie free) sheep were placed on these small pastures.... the new sheep also broke out with scrapie and passed it to offspring. I am not sure that TSE contaminated ground could ever be free of the agent!! A very frightening revelation!!!
---end personal email---end...tss
Infectivity surviving ashing to 600*C is (in my opinion) degradable but infective. based on Bown & Gajdusek, (1991), landfill and burial may be assumed to have a reduction factor of 98% (i.e. a factor of 50) over 3 years. CJD-infected brain-tissue remained infectious after storing at room-temperature for 22 months (Tateishi et al, 1988). Scrapie agent is known to remain viable after at least 30 months of desiccation (Wilson et al, 1950). and pastures that had been grazed by scrapie-infected sheep still appeared to be contaminated with scrapie agent three years after they were last occupied by sheep (Palsson, 1979).
Dr. Paul Brown Scrapie Soil Test BSE Inquiry Document
THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 28, 2019
BSE infectivity survives burial for five years with only limited spread
Using in vitro Prion replication for high sensitive detection of prions and prionlike proteins and for understanding mechanisms of transmission.
Claudio Soto Mitchell Center for Alzheimer's diseases and related Brain disorders, Department of Neurology, University of Texas Medical School at Houston.
Prion and prion-like proteins are misfolded protein aggregates with the ability to selfpropagate to spread disease between cells, organs and in some cases across individuals. I n T r a n s m i s s i b l e s p o n g i f o r m encephalopathies (TSEs), prions are mostly composed by a misfolded form of the prion protein (PrPSc), which propagates by transmitting its misfolding to the normal prion protein (PrPC). The availability of a procedure to replicate prions in the laboratory may be important to study the mechanism of prion and prion-like spreading and to develop high sensitive detection of small quantities of misfolded proteins in biological fluids, tissues and environmental samples. Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification (PMCA) is a simple, fast and efficient methodology to mimic prion replication in the test tube. PMCA is a platform technology that may enable amplification of any prion-like misfolded protein aggregating through a seeding/nucleation process. In TSEs, PMCA is able to detect the equivalent of one single molecule of infectious PrPSc and propagate prions that maintain high infectivity, strain properties and species specificity. Using PMCA we have been able to detect PrPSc in blood and urine of experimentally infected animals and humans affected by vCJD with high sensitivity and specificity. Recently, we have expanded the principles of PMCA to amplify amyloid-beta (Aβ) and alphasynuclein (α-syn) aggregates implicated in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, respectively. Experiments are ongoing to study the utility of this technology to detect Aβ and α-syn aggregates in samples of CSF and blood from patients affected by these diseases.
=========================
***>>> Recently, we have been using PMCA to study the role of environmental prion contamination on the horizontal spreading of TSEs. These experiments have focused on the study of the interaction of prions with plants and environmentally relevant surfaces. Our results show that plants (both leaves and roots) bind tightly to prions present in brain extracts and excreta (urine and feces) and retain even small quantities of PrPSc for long periods of time. Strikingly, ingestion of prioncontaminated leaves and roots produced disease with a 100% attack rate and an incubation period not substantially longer than feeding animals directly with scrapie brain homogenate. Furthermore, plants can uptake prions from contaminated soil and transport them to different parts of the plant tissue (stem and leaves). Similarly, prions bind tightly to a variety of environmentally relevant surfaces, including stones, wood, metals, plastic, glass, cement, etc. Prion contaminated surfaces efficiently transmit prion disease when these materials were directly injected into the brain of animals and strikingly when the contaminated surfaces were just placed in the animal cage. These findings demonstrate that environmental materials can efficiently bind infectious prions and act as carriers of infectivity, suggesting that they may play an important role in the horizontal transmission of the disease.
========================
Since its invention 13 years ago, PMCA has helped to answer fundamental questions of prion propagation and has broad applications in research areas including the food industry, blood bank safety and human and veterinary disease diagnosis.
New studies on the heat resistance of hamster-adapted scrapie agent: Threshold survival after ashing at 600°C suggests an inorganic template of replication
Prion Infected Meat-and-Bone Meal Is Still Infectious after Biodiesel Production
Detection of protease-resistant cervid prion protein in water from a CWD-endemic area
A Quantitative Assessment of the Amount of Prion Diverted to Category 1 Materials and Wastewater During Processing
Rapid assessment of bovine spongiform encephalopathy prion inactivation by heat treatment in yellow grease produced in the industrial manufacturing process of meat and bone meals
PPo4-4:
Survival and Limited Spread of TSE Infectivity after Burial
Discussion Classical scrapie is an environmentally transmissible disease because it has been reported in naïve, supposedly previously unexposed sheep placed in pastures formerly occupied by scrapie-infected sheep (4, 19, 20).
Although the vector for disease transmission is not known, soil is likely to be an important reservoir for prions (2) where – based on studies in rodents – prions can adhere to minerals as a biologically active form (21) and remain infectious for more than 2 years (22).
Similarly, chronic wasting disease (CWD) has re-occurred in mule deer housed in paddocks used by infected deer 2 years earlier, which was assumed to be through foraging and soil consumption (23).
Our study suggested that the risk of acquiring scrapie infection was greater through exposure to contaminated wooden, plastic, and metal surfaces via water or food troughs, fencing, and hurdles than through grazing.
Drinking from a water trough used by the scrapie flock was sufficient to cause infection in sheep in a clean building.
Exposure to fences and other objects used for rubbing also led to infection, which supported the hypothesis that skin may be a vector for disease transmission (9).
The risk of these objects to cause infection was further demonstrated when 87% of 23 sheep presented with PrPSc in lymphoid tissue after grazing on one of the paddocks, which contained metal hurdles, a metal lamb creep and a water trough in contact with the scrapie flock up to 8 weeks earlier, whereas no infection had been demonstrated previously in sheep grazing on this paddock, when equipped with new fencing and field furniture.
When the contaminated furniture and fencing were removed, the infection rate dropped significantly to 8% of 12 sheep, with soil of the paddock as the most likely source of infection caused by shedding of prions from the scrapie-infected sheep in this paddock up to a week earlier.
This study also indicated that the level of contamination of field furniture sufficient to cause infection was dependent on two factors: stage of incubation period and time of last use by scrapie-infected sheep.
Drinking from a water trough that had been used by scrapie sheep in the predominantly pre-clinical phase did not appear to cause infection, whereas infection was shown in sheep drinking from the water trough used by scrapie sheep in the later stage of the disease.
It is possible that contamination occurred through shedding of prions in saliva, which may have contaminated the surface of the water trough and subsequently the water when it was refilled.
Contamination appeared to be sufficient to cause infection only if the trough was in contact with sheep that included clinical cases.
Indeed, there is an increased risk of bodily fluid infectivity with disease progression in scrapie (24) and CWD (25) based on PrPSc detection by sPMCA.
Although ultraviolet light and heat under natural conditions do not inactivate prions (26), furniture in contact with the scrapie flock, which was assumed to be sufficiently contaminated to cause infection, did not act as vector for disease if not used for 18 months, which suggest that the weathering process alone was sufficient to inactivate prions.
PrPSc detection by sPMCA is increasingly used as a surrogate for infectivity measurements by bioassay in sheep or mice.
In this reported study, however, the levels of PrPSc present in the environment were below the limit of detection of the sPMCA method, yet were still sufficient to cause infection of in-contact animals.
In the present study, the outdoor objects were removed from the infected flock 8 weeks prior to sampling and were positive by sPMCA at very low levels (2 out of 37 reactions).
As this sPMCA assay also yielded 2 positive reactions out of 139 in samples from the scrapie-free farm, the sPMCA assay could not detect PrPSc on any of the objects above the background of the assay.
False positive reactions with sPMCA at a low frequency associated with de novo formation of infectious prions have been reported (27, 28).
This is in contrast to our previous study where we demonstrated that outdoor objects that had been in contact with the scrapie-infected flock up to 20 days prior to sampling harbored PrPSc that was detectable by sPMCA analysis [4 out of 15 reactions (12)] and was significantly more positive by the assay compared to analogous samples from the scrapie-free farm.
This discrepancy could be due to the use of a different sPMCA substrate between the studies that may alter the efficiency of amplification of the environmental PrPSc.
In addition, the present study had a longer timeframe between the objects being in contact with the infected flock and sampling, which may affect the levels of extractable PrPSc.
Alternatively, there may be potentially patchy contamination of this furniture with PrPSc, which may have been missed by swabbing.
The failure of sPMCA to detect CWD-associated PrP in saliva from clinically affected deer despite confirmation of infectivity in saliva-inoculated transgenic mice was associated with as yet unidentified inhibitors in saliva (29), and it is possible that the sensitivity of sPMCA is affected by other substances in the tested material.
In addition, sampling of amplifiable PrPSc and subsequent detection by sPMCA may be more difficult from furniture exposed to weather, which is supported by the observation that PrPSc was detected by sPMCA more frequently in indoor than outdoor furniture (12).
A recent experimental study has demonstrated that repeated cycles of drying and wetting of prion-contaminated soil, equivalent to what is expected under natural weathering conditions, could reduce PMCA amplification efficiency and extend the incubation period in hamsters inoculated with soil samples (30).
This seems to apply also to this study even though the reduction in infectivity was more dramatic in the sPMCA assays than in the sheep model.
Sheep were not kept until clinical end-point, which would have enabled us to compare incubation periods, but the lack of infection in sheep exposed to furniture that had not been in contact with scrapie sheep for a longer time period supports the hypothesis that prion degradation and subsequent loss of infectivity occurs even under natural conditions.
In conclusion, the results in the current study indicate that removal of furniture that had been in contact with scrapie-infected animals should be recommended, particularly since cleaning and decontamination may not effectively remove scrapie infectivity (31), even though infectivity declines considerably if the pasture and the field furniture have not been in contact with scrapie-infected sheep for several months. As sPMCA failed to detect PrPSc in furniture that was subjected to weathering, even though exposure led to infection in sheep, this method may not always be reliable in predicting the risk of scrapie infection through environmental contamination.
These results suggest that the VRQ/VRQ sheep model may be more sensitive than sPMCA for the detection of environmentally associated scrapie, and suggest that extremely low levels of scrapie contamination are able to cause infection in susceptible sheep genotypes.
Keywords: classical scrapie, prion, transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, sheep, field furniture, reservoir, serial protein misfolding cyclic amplification
Wednesday, December 16, 2015
*** Objects in contact with classical scrapie sheep act as a reservoir for scrapie transmission ***
WEDNESDAY, MARCH 13, 2019
CWD, TSE, PRION, MATERNAL mother to offspring, testes, epididymis, seminal fluid, and blood
Subject: Prion 2019 Conference
See full Prion 2019 Conference Abstracts
see scientific program and follow the cwd studies here;
Thursday, May 23, 2019
Prion 2019 Emerging Concepts CWD, BSE, SCRAPIE, CJD, SCIENTIFIC PROGRAM Schedule and Abstracts
THURSDAY, DECEMBER 19, 2019
TSE surveillance statistics exotic species and domestic cats Update December 2019
MONDAY, DECEMBER 16, 2019
Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion aka mad cow type disease in cervid Zoonosis Update
***> ''In particular the US data do not clearly exclude the possibility of human (sporadic or familial) TSE development due to consumption of venison. The Working Group thus recognizes a potential risk to consumers if a TSE would be present in European cervids.'' Scientific opinion on chronic wasting disease (II) <***
What if?
> However, to date, no CWD infections have been reported in people.
key word here is ‘reported’. science has shown that CWD in humans will look like sporadic CJD. SO, how can one assume that CWD has not already transmitted to humans? they can’t, and it’s as simple as that. from all recorded science to date, CWD has already transmitted to humans, and it’s being misdiagnosed as sporadic CJD. …terry
*** LOOKING FOR CWD IN HUMANS AS nvCJD or as an ATYPICAL CJD, LOOKING IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES $$$ ***
*** These results would seem to suggest that CWD does indeed have zoonotic potential, at least as judged by the compatibility of CWD prions and their human PrPC target. Furthermore, extrapolation from this simple in vitro assay suggests that if zoonotic CWD occurred, it would most likely effect those of the PRNP codon 129-MM genotype and that the PrPres type would be similar to that found in the most common subtype of sCJD (MM1).***
Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion aka mad deer disease zoonosis
We hypothesize that:
(1) The classic CWD prion strain can infect humans at low levels in the brain and peripheral lymphoid tissues;
(2) The cervid-to-human transmission barrier is dependent on the cervid prion strain and influenced by the host (human) prion protein (PrP) primary sequence;
(3) Reliable essays can be established to detect CWD infection in humans; and
(4) CWD transmission to humans has already occurred. We will test these hypotheses in 4 Aims using transgenic (Tg) mouse models and complementary in vitro approaches.
ZOONOTIC CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE CWD TSE PRION UPDATE
Prion 2017 Conference
First evidence of intracranial and peroral transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) into Cynomolgus macaques: a work in progress Stefanie Czub1, Walter Schulz-Schaeffer2, Christiane Stahl-Hennig3, Michael Beekes4, Hermann Schaetzl5 and Dirk Motzkus6 1
University of Calgary Faculty of Veterinary Medicine/Canadian Food Inspection Agency; 2Universitatsklinikum des Saarlandes und Medizinische Fakultat der Universitat des Saarlandes; 3 Deutsches Primaten Zentrum/Goettingen; 4 Robert-Koch-Institut Berlin; 5 University of Calgary Faculty of Veterinary Medicine; 6 presently: Boehringer Ingelheim Veterinary Research Center; previously: Deutsches Primaten Zentrum/Goettingen
This is a progress report of a project which started in 2009. 21 cynomolgus macaques were challenged with characterized CWD material from white-tailed deer (WTD) or elk by intracerebral (ic), oral, and skin exposure routes. Additional blood transfusion experiments are supposed to assess the CWD contamination risk of human blood product. Challenge materials originated from symptomatic cervids for ic, skin scarification and partially per oral routes (WTD brain). Challenge material for feeding of muscle derived from preclinical WTD and from preclinical macaques for blood transfusion experiments. We have confirmed that the CWD challenge material contained at least two different CWD agents (brain material) as well as CWD prions in muscle-associated nerves.
Here we present first data on a group of animals either challenged ic with steel wires or per orally and sacrificed with incubation times ranging from 4.5 to 6.9 years at postmortem. Three animals displayed signs of mild clinical disease, including anxiety, apathy, ataxia and/or tremor. In four animals wasting was observed, two of those had confirmed diabetes. All animals have variable signs of prion neuropathology in spinal cords and brains and by supersensitive IHC, reaction was detected in spinal cord segments of all animals. Protein misfolding cyclic amplification (PMCA), real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuiC) and PET-blot assays to further substantiate these findings are on the way, as well as bioassays in bank voles and transgenic mice.
At present, a total of 10 animals are sacrificed and read-outs are ongoing. Preclinical incubation of the remaining macaques covers a range from 6.4 to 7.10 years. Based on the species barrier and an incubation time of > 5 years for BSE in macaques and about 10 years for scrapie in macaques, we expected an onset of clinical disease beyond 6 years post inoculation.
PRION 2017 DECIPHERING NEURODEGENERATIVE DISORDERS
PRION 2018 CONFERENCE
Oral transmission of CWD into Cynomolgus macaques: signs of atypical disease, prion conversion and infectivity in macaques and bio-assayed transgenic mice
Hermann M. Schatzl, Samia Hannaoui, Yo-Ching Cheng, Sabine Gilch (Calgary Prion Research Unit, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada) Michael Beekes (RKI Berlin), Walter Schulz-Schaeffer (University of Homburg/Saar, Germany), Christiane Stahl-Hennig (German Primate Center) & Stefanie Czub (CFIA Lethbridge).
To date, BSE is the only example of interspecies transmission of an animal prion disease into humans. The potential zoonotic transmission of CWD is an alarming issue and was addressed by many groups using a variety of in vitro and in vivo experimental systems. Evidence from these studies indicated a substantial, if not absolute, species barrier, aligning with the absence of epidemiological evidence suggesting transmission into humans. Studies in non-human primates were not conclusive so far, with oral transmission into new-world monkeys and no transmission into old-world monkeys. Our consortium has challenged 18 Cynomolgus macaques with characterized CWD material, focusing on oral transmission with muscle tissue. Some macaques have orally received a total of 5 kg of muscle material over a period of 2 years.
After 5-7 years of incubation time some animals showed clinical symptoms indicative of prion disease, and prion neuropathology and PrPSc deposition were detected in spinal cord and brain of some euthanized animals. PrPSc in immunoblot was weakly detected in some spinal cord materials and various tissues tested positive in RT-QuIC, including lymph node and spleen homogenates. To prove prion infectivity in the macaque tissues, we have intracerebrally inoculated 2 lines of transgenic mice, expressing either elk or human PrP. At least 3 TgElk mice, receiving tissues from 2 different macaques, showed clinical signs of a progressive prion disease and brains were positive in immunoblot and RT-QuIC. Tissues (brain, spinal cord and spleen) from these and pre-clinical mice are currently tested using various read-outs and by second passage in mice. Transgenic mice expressing human PrP were so far negative for clear clinical prion disease (some mice >300 days p.i.). In parallel, the same macaque materials are inoculated into bank voles.
Taken together, there is strong evidence of transmissibility of CWD orally into macaques and from macaque tissues into transgenic mouse models, although with an incomplete attack rate.
The clinical and pathological presentation in macaques was mostly atypical, with a strong emphasis on spinal cord pathology.
Our ongoing studies will show whether the transmission of CWD into macaques and passage in transgenic mice represents a form of non-adaptive prion amplification, and whether macaque-adapted prions have the potential to infect mice expressing human PrP.
Our ongoing studies will show whether the transmission of CWD into macaques and passage in transgenic mice represents a form of non-adaptive prion amplification, and whether macaque-adapted prions have the potential to infect mice expressing human PrP.
The notion that CWD can be transmitted orally into both new-world and old-world non-human primates asks for a careful reevaluation of the zoonotic risk of CWD..
***> The notion that CWD can be transmitted orally into both new-world and old-world non-human primates asks for a careful reevaluation of the zoonotic risk of CWD. <***
READING OVER THE PRION 2018 ABSTRACT BOOK, LOOKS LIKE THEY FOUND THAT from this study ;
P190 Human prion disease mortality rates by occurrence of chronic wasting disease in freeranging cervids, United States
Abrams JY (1), Maddox RA (1), Schonberger LB (1), Person MK (1), Appleby BS (2), Belay ED (1) (1) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, Atlanta, GA, USA (2) Case Western Reserve University, National Prion Disease Pathology Surveillance Center (NPDPSC), Cleveland, OH, USA..
SEEMS THAT THEY FOUND Highly endemic states had a higher rate of prion disease mortality compared to non-CWD
states.
states.
AND ANOTHER STUDY;
P172 Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Prion Disease
Wang H(1), Cohen M(1), Appleby BS(1,2) (1) University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, Cleveland, Ohio (2) National Prion Disease Pathology Surveillance Center, Cleveland, Ohio..
IN THIS STUDY, THERE WERE autopsy-proven prion cases from the National Prion Disease Pathology Surveillance Center that were diagnosed between September 2016 to March 2017,
AND
included 104 patients. SEEMS THEY FOUND THAT The most common sCJD subtype was MV1-2 (30%), followed by MM1-2 (20%),
AND
THAT The Majority of cases were male (60%), AND half of them had exposure to wild game.
snip…
see more on Prion 2017 Macaque study from Prion 2017 Conference and other updated science on cwd tse prion zoonosis below…terry
PRION 2019 ABSTRACTS
1. Interspecies transmission of the chronic wasting disease agent
Justin Greenlee
Virus and Prion Research Unit, National Animal Disease Center, USDA Agriculture Research Service
ABSTRACT
The presentation will summarize the results of various studies conducted at our research center that assess the transmissibility of the chronic wasting disease (CWD) agent to cattle, pigs, raccoons, goats, and sheep. This will include specifics of the relative attack rates, clinical signs, and microscopic lesions with emphasis on how to differentiate cross-species transmission of the CWD agent from the prion diseases that naturally occur in hosts such as cattle or sheep. Briefly, the relative difficulty of transmitting the CWD agent to sheep and goats will be contrasted with the relative ease of transmitting the scrapie agent to white-tailed deer.
53. Evaluation of the inter-species transmission potential of different CWD isolates
Rodrigo Moralesa, Carlos Kramma,b, Paulina Sotoa, Adam Lyona, Sandra Pritzkowa, Claudio Sotoa
aMitchell Center for Alzheimer’s disease and Related Brain Disorders, Dept. of Neurology, McGovern School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, TX, USA; bFacultad de Medicina, Universidad de los Andes, Santiago, Chile
ABSTRACT
Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) has reached epidemic proportions in North America and has been identified in South Korea and Northern Europe. CWD-susceptible cervid species are known to share habitats with humans and other animals entering the human food chain. At present, the potential of CWD to infect humans and other animal species is not completely clear. The exploration of this issue acquires further complexity considering the differences in the prion protein sequence due to species-specific variations and polymorphic changes within species. While several species of cervids are naturally affected by CWD, white-tailed deer (WTD) is perhaps the most relevant due to its extensive use in hunting and as a source of food. Evaluation of inter-species prion infections using animals or mouse models is costly and time consuming. We and others have shown that the Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification (PMCA) technology reproduces, in an accelerated and inexpensive manner, the inter-species transmission of prions while preserving the strain features of the input PrPSc. In this work, we tested the potential of different WTD-derived CWD isolates to transmit to humans and other animal species relevant for human consumption using PMCA. For these experiments, CWD isolates homozygous for the most common WTD-PrP polymorphic changes (G96S) were used (96SS variant obtained from a pre-symptomatic prion infected WTD). Briefly, 96GG and 96SS CWD prions were adapted in homologous or heterologous substrate by PMCA through several (15) rounds. End products, as well as intermediates across the process, were tested for their inter-species transmission potentials. A similar process was followed to assess seed-templated misfolding of ovine, porcine, and bovine PrPC. Our results show differences on the inter-species transmission potentials of the four adapted materials generated (PrPC/PrPSc polymorphic combinations), being the homologous combinations of seed/substrate the ones with the greater apparent zoonotic potential. Surprisingly, 96SS prions adapted in homologous substrate were the ones showing the easiest potential to template PrPC misfolding from other animal species. In summary, our results show that a plethora of different CWD isolates, each comprising different potentials for inter-species transmission, may exist in the environment. These experiments may help to clarify an uncertain and potentially worrisome public health issue. Additional research in this area may be useful to advise on the design of regulations intended to stop the spread of CWD and predict unwanted zoonotic events.
56. Understanding chronic wasting disease spread potential for at-risk species
Catherine I. Cullingham, Anh Dao, Debbie McKenzie and David W. Coltman
Department of Biological Sciences, University of Alberta, Edmonton AB, Canada
CONTACT Catherine I. Cullingham cathy.cullingham@ualberta.ca
ABSTRACT
Genetic variation can be linked to susceptibility or resistance to a disease, and this information can help to better understand spread-risk in a population. Wildlife disease incidence is increasing, and this is resulting in negative impacts on the economy, biodiversity, and in some instances, human health. If we can find genetic variation that helps to inform which individuals are susceptible, then we can use this information on at-risk populations to better manage negative consequences. Chronic wasting disease, a fatal, transmissible spongiform encephalopathy of cervids (both wild and captive), continues to spread geographically, which has resulted in an increasing host-range. The disease agent (PrPCWD) is a misfolded conformer of native cellular protein (PrPC). In Canada, the disease is endemic in Alberta and Saskatchewan, infecting primarily mule deer and white-tail deer, with a smaller impact on elk and moose populations. As the extent of the endemic area continues to expand, additional species will be exposed to this disease, including bison, bighorn sheep, mountain goat, and pronghorn antelope. To better understand the potential spread-risk among these species, we reviewed the current literature on species that have been orally exposed to CWD to identify susceptible and resistant species. We then compared the amino acid polymorphisms of PrPC among these species to determine whether any sites were linked to susceptibility or resistance to CWD infection. We sequenced the entire PrP coding region in 578 individuals across at-risk populations to evaluate their potential susceptibility. Three amino acid sites (97, 170, and 174; human numbering) were significantly associated with susceptibility, but these were not fully discriminating. All but one species among the resistant group shared the same haplotype, and the same for the susceptible species. For the at-risk species, bison had the resistant haplotype, while bighorn sheep and mountain goats were closely associated with the resistant type. Pronghorn antelope and a newly identified haplotype in moose differed from the susceptible haplotype, but were still closely associated with it. These data suggest pronghorn antelope will be susceptible to CWD while bison are likely to be resistant. Based on this data, recommendations can be made regarding species to be monitored for possible CWD infection.
KEYWORDS: Chronic wasting disease; Prnp; wildlife disease; population genetics; ungulates
Thursday, May 23, 2019
Prion 2019 Emerging Concepts CWD, BSE, SCRAPIE, CJD, SCIENTIFIC PROGRAM Schedule and Abstracts
see full Prion 2019 Conference Abstracts
THURSDAY, OCTOBER 04, 2018
Cervid to human prion transmission 5R01NS088604-04 Update
snip…full text;
SATURDAY, FEBRUARY 09, 2019
Experts: Yes, chronic wasting disease in deer is a public health issue — for people
SATURDAY, FEBRUARY 23, 2019
Chronic Wasting Disease CWD TSE Prion and THE FEAST 2003 CDC an updated review of the science 2019
TUESDAY, NOVEMBER 04, 2014
Six-year follow-up of a point-source exposure to CWD contaminated venison in an Upstate New York community: risk behaviours and health outcomes 2005–2011
Authors, though, acknowledged the study was limited in geography and sample size and so it couldn't draw a conclusion about the risk to humans. They recommended more study. Dr. Ermias Belay was the report's principal author but he said New York and Oneida County officials are following the proper course by not launching a study. "There's really nothing to monitor presently. No one's sick," Belay said, noting the disease's incubation period in deer and elk is measured in years. "
Transmission Studies
Mule deer transmissions of CWD were by intracerebral inoculation and compared with natural cases {the following was written but with a single line marked through it ''first passage (by this route)}....TSS
resulted in a more rapidly progressive clinical disease with repeated episodes of synocopy ending in coma. One control animal became affected, it is believed through contamination of inoculum (?saline). Further CWD transmissions were carried out by Dick Marsh into ferret, mink and squirrel monkey. Transmission occurred in ALL of these species with the shortest incubation period in the ferret.
snip....
Prion Infectivity in Fat of Deer with Chronic Wasting Disease▿
Brent Race#, Kimberly Meade-White#, Richard Race and Bruce Chesebro* + Author Affiliations
In mice, prion infectivity was recently detected in fat. Since ruminant fat is consumed by humans and fed to animals, we determined infectivity titers in fat from two CWD-infected deer. Deer fat devoid of muscle contained low levels of CWD infectivity and might be a risk factor for prion infection of other species.
Prions in Skeletal Muscles of Deer with Chronic Wasting Disease
Here bioassays in transgenic mice expressing cervid prion protein revealed the presence of infectious prions in skeletal muscles of CWD-infected deer, demonstrating that humans consuming or handling meat from CWD-infected deer are at risk to prion exposure.
*** now, let’s see what the authors said about this casual link, personal communications years ago, and then the latest on the zoonotic potential from CWD to humans from the TOKYO PRION 2016 CONFERENCE.
see where it is stated NO STRONG evidence. so, does this mean there IS casual evidence ???? “Our conclusion stating that we found no strong evidence of CWD transmission to humans”
From: TSS (216-119-163-189.ipset45.wt.net)
Subject: CWD aka MAD DEER/ELK TO HUMANS ???
Date: September 30, 2002 at 7:06 am PST
From: "Belay, Ermias"
To: Cc: "Race, Richard (NIH)" ; ; "Belay, Ermias"
Sent: Monday, September 30, 2002 9:22 AM
Subject: RE: TO CDC AND NIH - PUB MED- 3 MORE DEATHS - CWD - YOUNG HUNTERS
Dear Sir/Madam,
In the Archives of Neurology you quoted (the abstract of which was attached to your email), we did not say CWD in humans will present like variant CJD.. That assumption would be wrong. I encourage you to read the whole article and call me if you have questions or need more clarification (phone: 404-639-3091). Also, we do not claim that "no-one has ever been infected with prion disease from eating venison." Our conclusion stating that we found no strong evidence of CWD transmission to humans in the article you quoted or in any other forum is limited to the patients we investigated.
Ermias Belay, M.D. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
-----Original Message-----
From: Sent: Sunday, September 29, 2002 10:15 AM
Subject: TO CDC AND NIH - PUB MED- 3 MORE DEATHS - CWD - YOUNG HUNTERS
Sunday, November 10, 2002 6:26 PM .......snip........end..............TSS
Thursday, April 03, 2008
A prion disease of cervids: Chronic wasting disease 2008 1: Vet Res. 2008 Apr 3;39(4):41 A prion disease of cervids: Chronic wasting disease Sigurdson CJ.
snip...
*** twenty-seven CJD patients who regularly consumed venison were reported to the Surveillance Center***,
snip... full text ;
> However, to date, no CWD infections have been reported in people.
sporadic, spontaneous CJD, 85%+ of all human TSE, just not just happen. never in scientific literature has this been proven.
if one looks up the word sporadic or spontaneous at pubmed, you will get a laundry list of disease that are classified in such a way;
sporadic = 54,983 hits https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=sporadic
spontaneous = 325,650 hits https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=spontaneous
key word here is 'reported'. science has shown that CWD in humans will look like sporadic CJD. SO, how can one assume that CWD has not already transmitted to humans? they can't, and it's as simple as that. from all recorded science to date, CWD has already transmitted to humans, and it's being misdiagnosed as sporadic CJD. ...terry
*** LOOKING FOR CWD IN HUMANS AS nvCJD or as an ATYPICAL CJD, LOOKING IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES $$$ ***
*** These results would seem to suggest that CWD does indeed have zoonotic potential, at least as judged by the compatibility of CWD prions and their human PrPC target. Furthermore, extrapolation from this simple in vitro assay suggests that if zoonotic CWD occurred, it would most likely effect those of the PRNP codon 129-MM genotype and that the PrPres type would be similar to that found in the most common subtype of sCJD (MM1).***
FRIDAY, JULY 26, 2019
Chronic Wasting Disease in Cervids: Implications for Prion Transmission to Humans and Other Animal Species
TUESDAY, JANUARY 21, 2020
***> 2004 European Commission Chronic wasting disease AND TISSUES THAT MIGHT CARRY A RISK FOR HUMAN FOOD AND ANIMAL FEED CHAINS REPORT UPDATED 2020
***> In conclusion, sensory symptoms and loss of reflexes in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome can be explained by neuropathological changes in the spinal cord. We conclude that the sensory symptoms and loss of lower limb reflexes in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome is due to pathology in the caudal spinal cord. <***
***> The clinical and pathological presentation in macaques was mostly atypical, with a strong emphasis on spinal cord pathology.<***
***> The notion that CWD can be transmitted orally into both new-world and old-world non-human primates asks for a careful reevaluation of the zoonotic risk of CWD. <***
***> All animals have variable signs of prion neuropathology in spinal cords and brains and by supersensitive IHC, reaction was detected in spinal cord segments of all animals.<***
***> In particular the US data do not clearly exclude the possibility of human (sporadic or familial) TSE development due to consumption of venison. The Working Group thus recognizes a potential risk to consumers if a TSE would be present in European cervids.'' Scientific opinion on chronic wasting disease (II) <***
FRIDAY, OCTOBER 25, 2019
Experts testify United States is underprepared for bioterrorism threats Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy TSE Prion disease
***Moreover, sporadic disease has never been observed in breeding colonies or primate research laboratories, most notably among hundreds of animals over several decades of study at the National Institutes of Health25, and in nearly twenty older animals continuously housed in our own facility.***
Even if the prevailing view is that sporadic CJD is due to the spontaneous formation of CJD prions, it remains possible that its apparent sporadic nature may, at least in part, result from our limited capacity to identify an environmental origin.
https://www.nature.com/articles/srep11573
O.05: Transmission of prions to primates after extended silent incubation periods: Implications for BSE and scrapie risk assessment in human populations
Emmanuel Comoy, Jacqueline Mikol, Valerie Durand, Sophie Luccantoni, Evelyne Correia, Nathalie Lescoutra, Capucine Dehen, and Jean-Philippe Deslys Atomic Energy Commission; Fontenay-aux-Roses, France
Prion diseases (PD) are the unique neurodegenerative proteinopathies reputed to be transmissible under field conditions since decades. The transmission of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) to humans evidenced that an animal PD might be zoonotic under appropriate conditions. Contrarily, in the absence of obvious (epidemiological or experimental) elements supporting a transmission or genetic predispositions, PD, like the other proteinopathies, are reputed to occur spontaneously (atpical animal prion strains, sporadic CJD summing 80% of human prion cases).
Non-human primate models provided the first evidences supporting the transmissibiity of human prion strains and the zoonotic potential of BSE. Among them, cynomolgus macaques brought major information for BSE risk assessment for human health (Chen, 2014), according to their phylogenetic proximity to humans and extended lifetime. We used this model to assess the zoonotic potential of other animal PD from bovine, ovine and cervid origins even after very long silent incubation periods.
*** We recently observed the direct transmission of a natural classical scrapie isolate to macaque after a 10-year silent incubation period,
***with features similar to some reported for human cases of sporadic CJD, albeit requiring fourfold long incubation than BSE. Scrapie, as recently evoked in humanized mice (Cassard, 2014),
***is the third potentially zoonotic PD (with BSE and L-type BSE),
***thus questioning the origin of human sporadic cases.
We will present an updated panorama of our different transmission studies and discuss the implications of such extended incubation periods on risk assessment of animal PD for human health.
===============
***thus questioning the origin of human sporadic cases***
===============
***our findings suggest that possible transmission risk of H-type BSE to sheep and human. Bioassay will be required to determine whether the PMCA products are infectious to these animals.
==============
https://prion2015.files.wordpress.com/2015/05/prion2015abstracts.pdf
***Transmission data also revealed that several scrapie prions propagate in HuPrP-Tg mice with efficiency comparable to that of cattle BSE. While the efficiency of transmission at primary passage was low, subsequent passages resulted in a highly virulent prion disease in both Met129 and Val129 mice.
***Transmission of the different scrapie isolates in these mice leads to the emergence of prion strain phenotypes that showed similar characteristics to those displayed by MM1 or VV2 sCJD prion.
***These results demonstrate that scrapie prions have a zoonotic potential and raise new questions about the possible link between animal and human prions.
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/19336896.2016.1163048?journalCode=kprn20
Prion diseases (PD) are the unique neurodegenerative proteinopathies reputed to be transmissible under field conditions since decades. The transmission of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) to humans evidenced that an animal PD might be zoonotic under appropriate conditions. Contrarily, in the absence of obvious (epidemiological or experimental) elements supporting a transmission or genetic predispositions, PD, like the other proteinopathies, are reputed to occur spontaneously (atpical animal prion strains, sporadic CJD summing 80% of human prion cases).
Non-human primate models provided the first evidences supporting the transmissibiity of human prion strains and the zoonotic potential of BSE. Among them, cynomolgus macaques brought major information for BSE risk assessment for human health (Chen, 2014), according to their phylogenetic proximity to humans and extended lifetime. We used this model to assess the zoonotic potential of other animal PD from bovine, ovine and cervid origins even after very long silent incubation periods.
*** We recently observed the direct transmission of a natural classical scrapie isolate to macaque after a 10-year silent incubation period,
***with features similar to some reported for human cases of sporadic CJD, albeit requiring fourfold long incubation than BSE. Scrapie, as recently evoked in humanized mice (Cassard, 2014),
***is the third potentially zoonotic PD (with BSE and L-type BSE),
***thus questioning the origin of human sporadic cases.
We will present an updated panorama of our different transmission studies and discuss the implications of such extended incubation periods on risk assessment of animal PD for human health.
===============
***thus questioning the origin of human sporadic cases***
===============
***our findings suggest that possible transmission risk of H-type BSE to sheep and human. Bioassay will be required to determine whether the PMCA products are infectious to these animals.
==============
https://prion2015.files.wordpress.com/2015/05/prion2015abstracts.pdf
***Transmission data also revealed that several scrapie prions propagate in HuPrP-Tg mice with efficiency comparable to that of cattle BSE. While the efficiency of transmission at primary passage was low, subsequent passages resulted in a highly virulent prion disease in both Met129 and Val129 mice.
***Transmission of the different scrapie isolates in these mice leads to the emergence of prion strain phenotypes that showed similar characteristics to those displayed by MM1 or VV2 sCJD prion.
***These results demonstrate that scrapie prions have a zoonotic potential and raise new questions about the possible link between animal and human prions.
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/19336896.2016.1163048?journalCode=kprn20
PRION 2016 TOKYO
Saturday, April 23, 2016
SCRAPIE WS-01: Prion diseases in animals and zoonotic potential 2016
Prion. 10:S15-S21. 2016 ISSN: 1933-6896 printl 1933-690X online
Taylor & Francis
Prion 2016 Animal Prion Disease Workshop Abstracts
WS-01: Prion diseases in animals and zoonotic potential
Transmission of the different scrapie isolates in these mice leads to the emergence of prion strain phenotypes that showed similar characteristics to those displayed by MM1 or VV2 sCJD prion.
These results demonstrate that scrapie prions have a zoonotic potential and raise new questions about the possible link between animal and human prions.
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/19336896.2016.1163048?journalCode=kprn20
Title: Transmission of scrapie prions to primate after an extended silent incubation period)
*** In complement to the recent demonstration that humanized mice are susceptible to scrapie, we report here the first observation of direct transmission of a natural classical scrapie isolate to a macaque after a 10-year incubation period. Neuropathologic examination revealed all of the features of a prion disease: spongiform change, neuronal loss, and accumulation of PrPres throughout the CNS.
*** This observation strengthens the questioning of the harmlessness of scrapie to humans, at a time when protective measures for human and animal health are being dismantled and reduced as c-BSE is considered controlled and being eradicated.
*** Our results underscore the importance of precautionary and protective measures and the necessity for long-term experimental transmission studies to assess the zoonotic potential of other animal prion strains.
http://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publications.htm?SEQ_NO_115=313160
1: J Infect Dis 1980 Aug;142(2):205-8
Oral transmission of kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, and scrapie to nonhuman primates.
Gibbs CJ Jr, Amyx HL, Bacote A, Masters CL, Gajdusek DC.
Kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease of humans and scrapie disease of sheep and goats were transmitted to squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus) that were exposed to the infectious agents only by their nonforced consumption of known infectious tissues. The asymptomatic incubation period in the one monkey exposed to the virus of kuru was 36 months; that in the two monkeys exposed to the virus of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease was 23 and 27 months, respectively; and that in the two monkeys exposed to the virus of scrapie was 25 and 32 months, respectively. Careful physical examination of the buccal cavities of all of the monkeys failed to reveal signs or oral lesions. One additional monkey similarly exposed to kuru has remained asymptomatic during the 39 months that it has been under observation.
snip...
The successful transmission of kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, and scrapie by natural feeding to squirrel monkeys that we have reported provides further grounds for concern that scrapie-infected meat may occasionally give rise in humans to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
PMID: 6997404
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=6997404&dopt=Abstract
Recently the question has again been brought up as to whether scrapie is transmissible to man. This has followed reports that the disease has been transmitted to primates. One particularly lurid speculation (Gajdusek 1977) conjectures that the agents of scrapie, kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and transmissible encephalopathy of mink are varieties of a single "virus". The U.S. Department of Agriculture concluded that it could "no longer justify or permit scrapie-blood line and scrapie-exposed sheep and goats to be processed for human or animal food at slaughter or rendering plants" (ARC 84/77)" The problem is emphasised by the finding that some strains of scrapie produce lesions identical to the once which characterise the human dementias"
Whether true or not. the hypothesis that these agents might be transmissible to man raises two considerations. First, the safety of laboratory personnel requires prompt attention. Second, action such as the "scorched meat" policy of USDA makes the solution of the acrapie problem urgent if the sheep industry is not to suffer grievously.
snip...
76/10.12/4.6
Nature. 1972 Mar 10;236(5341):73-4.
Transmission of scrapie to the cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis).
Gibbs CJ Jr, Gajdusek DC.
Nature 236, 73 - 74 (10 March 1972); doi:10.1038/236073a0
Transmission of Scrapie to the Cynomolgus Monkey (Macaca fascicularis)
C. J. GIBBS jun. & D. C. GAJDUSEK
National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland
SCRAPIE has been transmitted to the cynomolgus, or crab-eating, monkey (Macaca fascicularis) with an incubation period of more than 5 yr from the time of intracerebral inoculation of scrapie-infected mouse brain. The animal developed a chronic central nervous system degeneration, with ataxia, tremor and myoclonus with associated severe scrapie-like pathology of intensive astroglial hypertrophy and proliferation, neuronal vacuolation and status spongiosus of grey matter. The strain of scrapie virus used was the eighth passage in Swiss mice (NIH) of a Compton strain of scrapie obtained as ninth intracerebral passage of the agent in goat brain, from Dr R. L. Chandler (ARC, Compton, Berkshire).
Wednesday, February 16, 2011
IN CONFIDENCE
SCRAPIE TRANSMISSION TO CHIMPANZEES
IN CONFIDENCE
A newly identified type of scrapie agent can naturally infect sheep with resistant PrP genotypes
Annick Le Dur*,?, Vincent Béringue*,?, Olivier Andréoletti?, Fabienne Reine*, Thanh Lan Laï*, Thierry Baron§, Bjørn Bratberg¶, Jean-Luc Vilotte?, Pierre Sarradin**, Sylvie L. Benestad¶, and Hubert Laude*,?? +Author Affiliations
*Virologie Immunologie Moléculaires and ?Génétique Biochimique et Cytogénétique, Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique, 78350 Jouy-en-Josas, France; ?Unité Mixte de Recherche, Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique-Ecole Nationale Vétérinaire de Toulouse, Interactions Hôte Agent Pathogène, 31066 Toulouse, France; §Agence Française de Sécurité Sanitaire des Aliments, Unité Agents Transmissibles Non Conventionnels, 69364 Lyon, France; **Pathologie Infectieuse et Immunologie, Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique, 37380 Nouzilly, France; and ¶Department of Pathology, National Veterinary Institute, 0033 Oslo, Norway
***Edited by Stanley B. Prusiner, University of California, San Francisco, CA (received for review March 21, 2005)
Abstract
Scrapie in small ruminants belongs to transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), or prion diseases, a family of fatal neurodegenerative disorders that affect humans and animals and can transmit within and between species by ingestion or inoculation. Conversion of the host-encoded prion protein (PrP), normal cellular PrP (PrPc), into a misfolded form, abnormal PrP (PrPSc), plays a key role in TSE transmission and pathogenesis. The intensified surveillance of scrapie in the European Union, together with the improvement of PrPSc detection techniques, has led to the discovery of a growing number of so-called atypical scrapie cases. These include clinical Nor98 cases first identified in Norwegian sheep on the basis of unusual pathological and PrPSc molecular features and "cases" that produced discordant responses in the rapid tests currently applied to the large-scale random screening of slaughtered or fallen animals. Worryingly, a substantial proportion of such cases involved sheep with PrP genotypes known until now to confer natural resistance to conventional scrapie. Here we report that both Nor98 and discordant cases, including three sheep homozygous for the resistant PrPARR allele (A136R154R171), efficiently transmitted the disease to transgenic mice expressing ovine PrP, and that they shared unique biological and biochemical features upon propagation in mice.
*** These observations support the view that a truly infectious TSE agent, unrecognized until recently, infects sheep and goat flocks and may have important implications in terms of scrapie control and public health.
OR
***The pathology features of Nor98 in the cerebellum of the affected sheep showed similarities with those of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans.
OR
*** Intriguingly, these conclusions suggest that some pathological features of Nor98 are reminiscent of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease.
OR here;
*** The discovery of previously unrecognized prion diseases in both humans and animals (i.e., Nor98 in small ruminants) demonstrates that the range of prion diseases might be wider than expected and raises crucial questions about the epidemiology and strain properties of these new forms. We are investigating this latter issue by molecular and biological comparison of VPSPr, GSS and Nor98.
VARIABLY PROTEASE-SENSITVE PRIONOPATHY IS TRANSMISSIBLE ...price of prion poker goes up again $
OR-10: Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy is transmissible in bank voles
Romolo Nonno,1 Michele Di Bari,1 Laura Pirisinu,1 Claudia D’Agostino,1 Stefano Marcon,1 Geraldina Riccardi,1 Gabriele Vaccari,1 Piero Parchi,2 Wenquan Zou,3 Pierluigi Gambetti,3 Umberto Agrimi1 1Istituto Superiore di Sanità; Rome, Italy; 2Dipartimento di Scienze Neurologiche, Università di Bologna; Bologna, Italy; 3Case Western Reserve University; Cleveland, OH USA
Background. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy (VPSPr) is a recently described “sporadic”neurodegenerative disease involving prion protein aggregation, which has clinical similarities with non-Alzheimer dementias, such as fronto-temporal dementia. Currently, 30 cases of VPSPr have been reported in Europe and USA, of which 19 cases were homozygous for valine at codon 129 of the prion protein (VV), 8 were MV and 3 were MM. A distinctive feature of VPSPr is the electrophoretic pattern of PrPSc after digestion with proteinase K (PK). After PK-treatment, PrP from VPSPr forms a ladder-like electrophoretic pattern similar to that described in GSS cases. The clinical and pathological features of VPSPr raised the question of the correct classification of VPSPr among prion diseases or other forms of neurodegenerative disorders. Here we report preliminary data on the transmissibility and pathological features of VPSPr cases in bank voles.
Materials and Methods. Seven VPSPr cases were inoculated in two genetic lines of bank voles, carrying either methionine or isoleucine at codon 109 of the prion protein (named BvM109 and BvI109, respectively). Among the VPSPr cases selected, 2 were VV at PrP codon 129, 3 were MV and 2 were MM. Clinical diagnosis in voles was confirmed by brain pathological assessment and western blot for PK-resistant PrPSc (PrPres) with mAbs SAF32, SAF84, 12B2 and 9A2.
Results. To date, 2 VPSPr cases (1 MV and 1 MM) gave positive transmission in BvM109. Overall, 3 voles were positive with survival time between 290 and 588 d post inoculation (d.p.i.). All positive voles accumulated PrPres in the form of the typical PrP27–30, which was indistinguishable to that previously observed in BvM109 inoculated with sCJDMM1 cases.
In BvI109, 3 VPSPr cases (2 VV and 1 MM) showed positive transmission until now. Overall, 5 voles were positive with survival time between 281 and 596 d.p.i.. In contrast to what observed in BvM109, all BvI109 showed a GSS-like PrPSc electrophoretic pattern, characterized by low molecular weight PrPres. These PrPres fragments were positive with mAb 9A2 and 12B2, while being negative with SAF32 and SAF84, suggesting that they are cleaved at both the C-terminus and the N-terminus. Second passages are in progress from these first successful transmissions.
Conclusions. Preliminary results from transmission studies in bank voles strongly support the notion that VPSPr is a transmissible prion disease. Interestingly, VPSPr undergoes divergent evolution in the two genetic lines of voles, with sCJD-like features in BvM109 and GSS-like properties in BvI109.
The discovery of previously unrecognized prion diseases in both humans and animals (i.e., Nor98 in small ruminants) demonstrates that the range of prion diseases might be wider than expected and raises crucial questions about the epidemiology and strain properties of these new forms. We are investigating this latter issue by molecular and biological comparison of VPSPr, GSS and Nor98.
WEDNESDAY, MAY 29, 2019
Incomplete inactivation of atypical scrapie following recommended autoclave decontamination procedures USDA HERE'S YOUR SIGN!
***> In conclusion, sensory symptoms and loss of reflexes in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome can be explained by neuropathological changes in the spinal cord. We conclude that the sensory symptoms and loss of lower limb reflexes in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome is due to pathology in the caudal spinal cord. <***
***> The clinical and pathological presentation in macaques was mostly atypical, with a strong emphasis on spinal cord pathology.<***
***> The notion that CWD can be transmitted orally into both new-world and old-world non-human primates asks for a careful reevaluation of the zoonotic risk of CWD. <***
***> All animals have variable signs of prion neuropathology in spinal cords and brains and by supersensitive IHC, reaction was detected in spinal cord segments of all animals.<***
***> In particular the US data do not clearly exclude the possibility of human (sporadic or familial) TSE development due to consumption of venison. The Working Group thus recognizes a potential risk to consumers if a TSE would be present in European cervids.'' Scientific opinion on chronic wasting disease (II) <***
THURSDAY, DECEMBER 12, 2019
Heidenhain Variant Creutzfeldt Jakob Disease hvCJD, sporadic spontaneous CJD and the TSE Prion December 14, 2019
MONDAY, FEBRUARY 25, 2019
***> MAD DOGS AND ENGLISHMEN BSE, SCRAPIE, CWD, CJD, TSE PRION A REVIEW 2019
Terry S. Singeltary Sr.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.