Mississippi MDWFP Chronic Wasting Disease: Present, Past, and Future
3/22/2018 2:11:33 PM
By William T. McKinley, MDWFP Deer Program Coodinator
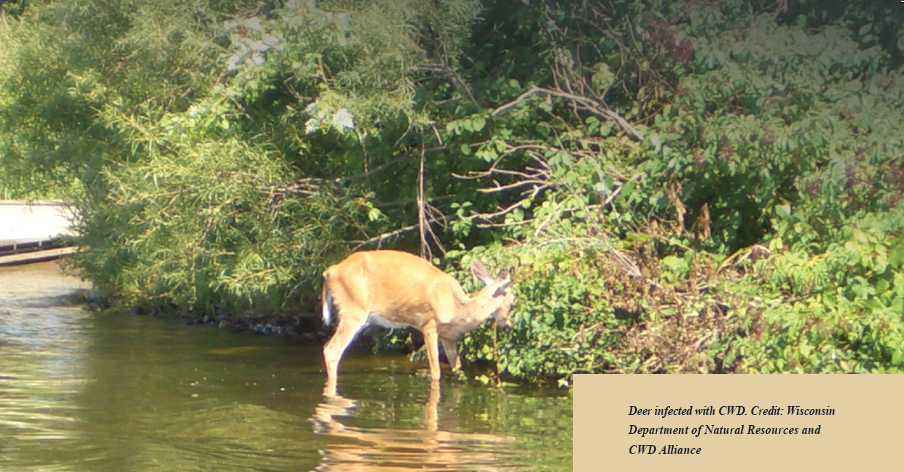


- transport of infected carcasses
- products manufactured or contaminated with prion-laden deer or elk urine, saliva, or feces
- movement of hay or grain crops contaminated with the CWD agent

Mineral licks: motivational factors for visitation and accompanying disease risk at communal use sites of elk and deer
Authors Authors and affiliations Michael J. LavelleEmail authorGregory E. PhillipsJustin W. FischerPatrick W. BurkeNathan W. SewardRandal S. StahlTracy A. NicholsBruce A. WunderKurt C. VerCauteren 1. 2. 3. 4.
Article First Online: 08 April 2014 258 Downloads 1 Citations
Abstract
Free-ranging cervids acquire most of their essential minerals through forage consumption, though occasionally seek other sources to account for seasonal mineral deficiencies. Mineral sources occur as natural geological deposits (i.e., licks) or as anthropogenic mineral supplements. In both scenarios, these sources commonly serve as focal sites for visitation. We monitored 11 licks in Rocky Mountain National Park, north-central Colorado, using trail cameras to quantify daily visitation indices (DVI) and soil consumption indices (SCI) for Rocky Mountain elk (Cervus elaphus) and mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) during summer 2006 and documented elk, mule deer, and moose (Alces alces) visiting licks. Additionally, soil samples were collected, and mineral concentrations were compared to discern levels that explain rates of visitation. Relationships between response variables; DVI and SCI, and explanatory variables; elevation class, moisture class, period of study, and concentrations of minerals were examined. We found that DVI and SCI were greatest at two wet, low-elevation licks exhibiting relatively high concentrations of manganese and sodium. Because cervids are known to seek Na from soils, we suggest our observed association of Mn with DVI and SCI was a likely consequence of deer and elk seeking supplemental dietary Na. Additionally, highly utilized licks such as these provide an area of concentrated cervid occupation and interaction, thus increasing risk for environmental transmission of infectious pathogens such as chronic wasting disease, which has been shown to be shed in the saliva, urine, and feces of infected cervids.
Keywords Cervus elaphus Chronic wasting disease Elk Geophagy Mineral lick Mule deer Odocoileus hemionus
https://rd.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10653-014-9600-0
Elk and Deer Use of Mineral Licks: Implications for Disease Transmission
Kurt C. VerCauteren1*, Michael J. Lavelle1, Gregory E. Phillips1, Justin W. Fischer1, and Randal S. Stahl1 1United States Department of Agriculture, Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, Wildlife Services, National Wildlife Research Center, 4101 LaPorte Avenue, Fort Collins, CO 80521-2154, USA *Cooresponding author e-mail: kurt.c.vercauteren@aphis.usda.gov
North American cervids require and actively seek out minerals to satisfy physiological requirements. Minerals required by free-ranging cervids exist within natural and artificial mineral licks that commonly serve as focal sites for cervids. Ingestion of soils contaminated with the agent that causes chronic wasting disease (CWD) may result in risk of contracting CWD. Our objective was to evaluate the extent and nature of use of mineral licks by CWD-susceptible cervid species. We used animal-activated cameras to monitor use of 18 mineral licks between 1 June and 16 October 2006 in Rocky Mountain National Park, north-central Colorado. We also assessed mineral concentrations at mineral licks to evaluate correlations between visitation rates and site-specific characteristics. We collected > 400,000 images of which 991 included elk, 293 included deer, and 6 included moose. We documented elk and deer participating in a variety of potentially risky behaviors (e.g., ingesting soil, ingesting water, defecating, urinating) while at mineral licks. Results from the mineral analyses combined with camera data revealed that visitation was highest at sodium-rich mineral licks. Mineral licks may play a role in disease transmission by acting as sites of increased interaction as well as reservoirs for deposition, accumulation, and ingestion of disease agents.
http://www.cwd-info.org/pdf/3rd_CWD_Symposium_utah.pdf
http://chronic-wasting-disease.blogspot.com/2009/08/third-international-cwd-symposium-july.html
***at present, no cervid PrP allele conferring absolute resistance to prion infection has been identified.
P-145 Estimating chronic wasting disease resistance in cervids using real time quaking- induced conversion
Nicholas J Haley1, Rachel Rielinqer2, Kristen A Davenport3, W. David Walter4, Katherine I O'Rourke5, Gordon Mitchell6, Juergen A Richt2 1 Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Midwestern University, United States; 2Department of Diagnostic Medicine and Pathobiology, Kansas State University; 3Prion Research Center; Colorado State University; 4U.S. Geological Survey, Pennsylvania Cooperative Fish and Wildlife Research Unit; 5Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture; 6Canadian Food Inspection Agency, National and OlE Reference Laboratory for Scrapie and CWD
In mammalian species, the susceptibility to prion diseases is affected, in part, by the sequence of the host's prion protein (PrP). In sheep, a gradation from scrapie susceptible to resistant has been established both in vivo and in vitro based on the amino acids present at PrP positions 136, 154, and 171, which has led to global breeding programs to reduce the prevalence of scrapie in domestic sheep. In cervids, resistance is commonly characterized as a delayed progression of chronic wasting disease (CWD); at present, no cervid PrP allele conferring absolute resistance to prion infection has been identified. To model the susceptibility of various naturally-occurring and hypothetical cervid PrP alleles in vitro, we compared the amplification rates and efficiency of various CWD isolates in recombinant PrPC using real time quaking-induced conversion. We hypothesized that amplification metrics of these isolates in cervid PrP substrates would correlate to in vivo susceptibility - allowing susceptibility prediction for alleles found at 10 frequency in nature, and that there would be an additive effect of multiple resistant codons in hypothetical alleles. Our studies demonstrate that in vitro amplification metrics predict in vivo susceptibility, and that alleles with multiple codons, each influencing resistance independently, do not necessarily contribute additively to resistance. Importantly, we found that the white-tailed deer 226K substrate exhibited the slowest amplification rate among those evaluated, suggesting that further investigation of this allele and its resistance in vivo are warranted to determine if absolute resistance to CWD is possible.
***at present, no cervid PrP allele conferring absolute resistance to prion infection has been identified.
PRION 2016 CONFERENCE TOKYO
http://prion2016.org/dl/newsletter_03.pdf
''There are no known familial or genetic TSEs of animals, although polymorphisms in the PRNP gene of some species (sheep for example) may influence the length of the incubation period and occurrence of disease.''
c) The commonest form of CJD occurs as a sporadic disease, the cause of which is unknown, although genetic factors (particularly the codon 129 polymorphism in the prion protein gene (PRNP)) influence disease susceptibility. The familial forms of human TSEs (see Box 1) appear to have a solely genetic origin and are closely associated with mutations or insertions in the PRNP gene. Most, but not all, of the familial forms of human TSEs have been transmitted experimentally to animals. There are no known familial or genetic TSEs of animals, although polymorphisms in the PRNP gene of some species (sheep for example) may influence the length of the incubation period and occurrence of disease.
https://www.gov.uk/government/uploa...nt_data/file/209755/Part_1_-_Introduction.pdf
''There are no known familial or genetic TSEs of animals, although polymorphisms in the PRNP gene of some species (sheep for example) may influence the length of the incubation period and occurrence of disease.''
c) The commonest form of CJD occurs as a sporadic disease, the cause of which is unknown, although genetic factors (particularly the codon 129 polymorphism in the prion protein gene (PRNP)) influence disease susceptibility. The familial forms of human TSEs (see Box 1) appear to have a solely genetic origin and are closely associated with mutations or insertions in the PRNP gene. Most, but not all, of the familial forms of human TSEs have been transmitted experimentally to animals. There are no known familial or genetic TSEs of animals, although polymorphisms in the PRNP gene of some species (sheep for example) may influence the length of the incubation period and occurrence of disease.
https://www.gov.uk/government/uploa...nt_data/file/209755/Part_1_-_Introduction.pdf
Subject: cwd genetic susceptibility
Genetic susceptibility to chronic wasting disease in free-ranging white-tailed deer: Complement component C1q and Prnp polymorphisms§
Julie A. Blanchong a, *, Dennis M. Heisey b , Kim T. Scribner c , Scot V. Libants d , Chad Johnson e , Judd M. Aiken e , Julia A. Langenberg f , Michael D. Samuel g
snip...
Identifying the genetic basis for heterogeneity in disease susceptibility or progression can improve our understanding of individual variation in disease susceptibility in both free-ranging and captive populations. What this individual variation in disease susceptibility means for the trajectory of disease in a population, however, is not straightforward. For example, the greater, but not complete, resistance to CWD in deer with at least one Serine (S) at amino acid 96 of the Prnp gene appears to be associated with slower progression of disease (e.g., Johnson et al., 2006; Keane et al., 2008a). If slower disease progression results in longer-lived, infected deer with longer periods of infectiousness, resistance may lead to increased disease transmission rates, higher prion concentrations in the environment, and increased prevalence, as has been observed in some captive deer herds (Miller et al., 2006; Keane et al., 2008a). Alternatively, if the slower progression of disease in resistant deer is not associated with longer periods of infectiousness, but might instead indicate a higher dose of PrPCWD is required for infection, transmission rates in the population could decline especially if, as in Wisconsin, deer suffer high rates of mortality from other sources (e.g., hunting). Clearly, determining the relationship between genetic susceptibility to infection, dose requirements, disease progression, and the period of PrPCWD infectiousness are key components for understanding the consequences of CWD to free-ranging populations.
http:// http://forest.wisc.edu/files/pdfs/samuel/2009%20blanchong%20et%20al%20genetic%20susceptibility%20chronic%20wasting.pdf
http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1083&context=nrem_pubs
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4667/epdf
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19336896.2015.1115179
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4964855/pdf/kprn-09-06-1115179.pdf
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1567134809001956?via=ihub
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4964855/
USDA TO PGC ONCE CAPTIVES ESCAPE
*** "it‘s no longer its business.”
http://chronic-wasting-disease.blogspot.com/2013/01/usda-to-pgc-once-captives-escape-its-no.html
”The occurrence of CWD must be viewed against the contest of the locations in which it occurred. It was an incidental and unwelcome complication of the respective wildlife research programmes. Despite it’s subsequent recognition as a new disease of cervids, therefore justifying direct investigation, no specific research funding was forthcoming. The USDA veiwed it as a wildlife problem and consequently not their province!” page 26.
https://web.archive.org/web/20060307063531/http://www.bseinquiry.gov.uk/files/mb/m11b/tab01.pdf
*** Spraker suggested an interesting explanation for the occurrence of CWD. The deer pens at the Foot Hills Campus were built some 30-40 years ago by a Dr. Bob Davis. At or abut that time, allegedly, some scrapie work was conducted at this site. When deer were introduced to the pens they occupied ground that had previously been occupied by sheep.
https://web.archive.org/web/20170126060744/http://collections.europarchive.org/tna/20080102193705/http://www.bseinquiry.gov.uk/files/mb/m11b/tab01.pdf
COLORADO THE ORIGIN OF CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE CWD TSE PRION?
*** Spraker suggested an interesting explanation for the occurrence of CWD. The deer pens at the Foot Hills Campus were built some 30-40 years ago by a Dr. Bob Davis. At or abut that time, allegedly, some scrapie work was conducted at this site. When deer were introduced to the pens they occupied ground that had previously been occupied by sheep.
IN CONFIDENCE, REPORT OF AN UNCONVENTIONAL SLOW VIRUS DISEASE IN ANIMALS IN THE USA 1989
http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20080102193705/http://www.bseinquiry.gov.uk/files/mb/m11b/tab01.pdf
Friday, January 17, 2014
*** Further, it was addressed that recently discussions have being held at OIE level on Chronic Wasting Disease of cervids.
2002 Singeltary vs O.I.E. on CWD to human risk factor ;
Subject: Re: CWD AMERICA ???
----- Original Message -----
>>> *** Further, it was addressed that recently discussions have being held at OIE level on Chronic Wasting Disease of cervids. <<<
> hello Dr. Jebara,
>
> many thanks for your swift and kind reply.
>
> if i am not mistaken, it was the same email address.
> it was 3 or 4 weeks ago i wrote, as it is, i don't
> save 'sent' emails anymore, unless very important.
>
> my main concern (besides the fact that a potential TSE
> has been in the USA cattle for some time, but the APHIS
> do not test to find), is that the CWD could very well be
> transmitting to humans, and i just did not see to much
> posted about it on OIE site.
>
> > Coming back to your question, Chronic Wasting Disease is not an OIE
>
> > listed disease. Please see OIE disease lists at
>
> http://www.oie.int/eng/maladies/en_classification.htm#ListeA).
>
> why is this TSE (CWD) not listed and followed as with BSE ?
>
> Article 1.1.3.2.
> 1. Countries shall make available to other countries, through the
> OIE, whatever information is necessary to minimise the spread of
> important animal diseases and to assist in achieving better worldwide
> control of these diseases.
>
> http://www.oie.int/eng/normes/MCode/A_00005.htm
>
> The USA CWD is an important animal disease.
>
> why is it not followed?
>
> > The decision to add or delete a disease from the OIE lists, come
>
> > through proposals made by Member Countries and it has to be adopted by
>
> > the International Committee.
>
> i _urgently_ suggest a proposal to the OIE to follow this disease very
> closely, and to propose _more_ testing in the USA for TSEs in the USA
> cattle...
>
> kindest regards,
> terry
>
> INFORMATION DEPT wrote:
>
> > Dear Sir,
> >
> > This is the first time that I receive your e-mail. To whom have you written
> > in the OIE or to which address?
> >
> > Coming back to your question, Chronic Wasting Disease is not an OIE listed
> > disease. Please see OIE disease lists at
> > http://www.oie.int/eng/maladies/en_classification.htm#ListeA).
> >
> > Countries should report to the OIE any disease even is not listed in the
> > OIE's lists in some conditions (example: an exceptional epidemiological
> > event). Please read Chapter 1.1.3 of the International animal health code to
> > have more information on disease notification and epidemiological
> > information agreed by OIE Member Countries at :
> > http://www.oie.int/eng/normes/MCode/A_00005.htm
> >
> > The decision to add or delete a disease from the OIE lists, come through
> > proposals made by Member Countries and it has to be adopted by the
> > International Committee.
> >
> > Hope that I answered to your question.
> >
> > Best regards.
> >
> > Dr Karim Ben Jebara
> > Head
> > Animal Health Information Department
> > OIE
> >
> >
> >
> > ----- Original Message -----
> > From: "Terry S. Singeltary Sr."
> > To:
> > Sent: Friday, July 12, 2002 6:18 PM
> > Subject: CWD AMERICA ???
> >
> >
> >
> >>I WROTE TO OIE RECENTLY ASKING 'WHY OIE DOES NOT FOLLOW CWD IN
> >>AMERICA' ? with no reply ? i am still seeking an answer ?
> >>
> >>many thanks,
> >>and kind regards,
> >>terry
=====================
Background
Alzheimer’s disease and Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy disease have both been around a long time, and was discovered in or around the same time frame, early 1900’s. Both diseases are incurable and debilitating brain disease, that are in the end, 100% fatal, with the incubation/clinical period of the Alzheimer’s disease being longer (most of the time) than the TSE prion disease. Symptoms are very similar, and pathology is very similar.
Methods
Through years of research, as a layperson, of peer review journals, transmission studies, and observations of loved ones and friends that have died from both Alzheimer’s and the TSE prion disease i.e. Heidenhain Variant Creutzfelt Jakob Disease CJD.
Results
I propose that Alzheimer’s is a TSE disease of low dose, slow, and long incubation disease, and that Alzheimer’s is Transmissible, and is a threat to the public via the many Iatrogenic routes and sources. It was said long ago that the only thing that disputes this, is Alzheimer’s disease transmissibility, or the lack of. The likelihood of many victims of Alzheimer’s disease from the many different Iatrogenic routes and modes of transmission as with the TSE prion disease.
Conclusions
There should be a Global Congressional Science round table event set up immediately to address these concerns from the many potential routes and sources of the TSE prion disease, including Alzheimer’s disease, and a emergency global doctrine put into effect to help combat the spread of Alzheimer’s disease via the medical, surgical, dental, tissue, and blood arena’s. All human and animal TSE prion disease, including Alzheimer’s should be made reportable in every state, and Internationally, WITH NO age restrictions. Until a proven method of decontamination and autoclaving is proven, and put forth in use universally, in all hospitals and medical, surgical arena’s, or the TSE prion agent will continue to spread. IF we wait until science and corporate politicians wait until politics lets science _prove_ this once and for all, and set forth regulations there from, we will all be exposed to the TSE Prion agents, if that has not happened already.
end...tss
Alzheimer’s disease and Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy prion disease, Iatrogenic, what if ?
source references ...end...tss
Hello Nicole,
by all means, please do use my poster. but I thought this was already taken care of, and I could not attend for my poster presentation, therefore, it was not going to be presented. I have some health issues and could not make the trip.
please see old correspondence below...
From: Nicole Sanders Sent: Tuesday, April 10, 2012 5:37 PM To: Terry S. Singeltary Sr. Subject: RE: re-submission
Dear Terry,
The decline of proposal number 30756 is registered in the system. Thank you for your consideration.
Best Regards,
Nicole
Nicole Sanders
Senior Specialist, Membership & Conference Programming
______________________________________
From: xxxx
To: Terry Singeltary
Sent: Saturday, December 05, 2009 9:09 AM
Subject: 14th ICID - abstract accepted for 'International Scientific Exchange'
Your preliminary abstract number: 670
Dear Mr. Singeltary,
On behalf of the Scientific Committee, I am pleased to inform you that your abstract
'Transmissible Spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) animal and human TSE in North America update October 2009'
WAS accepted for inclusion in the INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC EXCHANGE (ISE) section of the 14th International Congress on Infectious Diseases. Accordingly, your abstract will be included in the "Intl. Scientific Exchange abstract CD-rom" of the Congress which will be distributed to all participants.
Abstracts accepted for INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC EXCHANGE are NOT PRESENTED in the oral OR poster sessions.
Your abstract below was accepted for: INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC EXCHANGE
#0670: Transmissible Spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) animal and human TSE in North America update October 2009
Author: T. Singeltary; Bacliff, TX/US
Topic: Emerging Infectious Diseases Preferred type of presentation: International Scientific Exchange
This abstract has been ACCEPTED.
#0670: Transmissible Spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) animal and human TSE in North America update October 2009
Authors: T. Singeltary; Bacliff, TX/US
Title: Transmissible Spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) animal and human TSE in North America update October 2009
Body: Background
An update on atypical BSE and other TSE in North America. Please remember, the typical U.K. c-BSE, the atypical l-BSE (BASE), and h-BSE have all been documented in North America, along with the typical scrapie's, and atypical Nor-98 Scrapie, and to date, 2 different strains of CWD, and also TME. All these TSE in different species have been rendered and fed to food producing animals for humans and animals in North America (TSE in cats and dogs ?), and that the trading of these TSEs via animals and products via the USA and Canada has been immense over the years, decades.
Methods
12 years independent research of available data
Results
I propose that the current diagnostic criteria for human TSEs only enhances and helps the spreading of human TSE from the continued belief of the UKBSEnvCJD only theory in 2009. With all the science to date refuting it, to continue to validate this old myth, will only spread this TSE agent through a multitude of potential routes and sources i.e. consumption, medical i.e., surgical, blood, dental, endoscopy, optical, nutritional supplements, cosmetics etc.
Conclusion
I would like to submit a review of past CJD surveillance in the USA, and the urgent need to make all human TSE in the USA a reportable disease, in every state, of every age group, and to make this mandatory immediately without further delay. The ramifications of not doing so will only allow this agent to spread further in the medical, dental, surgical arena's. Restricting the reporting of CJD and or any human TSE is NOT scientific. Iatrogenic CJD knows NO age group, TSE knows no boundaries.
I propose as with Aguzzi, Asante, Collinge, Caughey, Deslys, Dormont, Gibbs, Gajdusek, Ironside, Manuelidis, Marsh, et al and many more, that the world of TSE Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy is far from an exact science, but there is enough proven science to date that this myth should be put to rest once and for all, and that we move forward with a new classification for human and animal TSE that would properly identify the infected species, the source species, and then the route.
Keywords: Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy Creutzfeldt Jakob Disease Prion
page 114 ;
http://ww2.isid.org/Downloads/14th_ICID_ISE_Abstracts.pdf
http://www.isid.org/14th_icid/
http://www.isid.org/publications/ICID_Archive.shtml
http://ww2.isid.org/Downloads/IMED2009_AbstrAuth.pdf
Neuropathology of iatrogenic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease and immunoassay of French cadaver-sourced growth hormone batches suggest possible transmission of tauopathy and long incubation periods for the transmission of Abeta pathology
http://tauopathies.blogspot.com/2017/12/neuropathology-of-iatrogenic.html

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home